A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Map of Europe in 1810
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Map of Europe in 1810
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Map of Europe in 1810. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Map of Europe in 1810
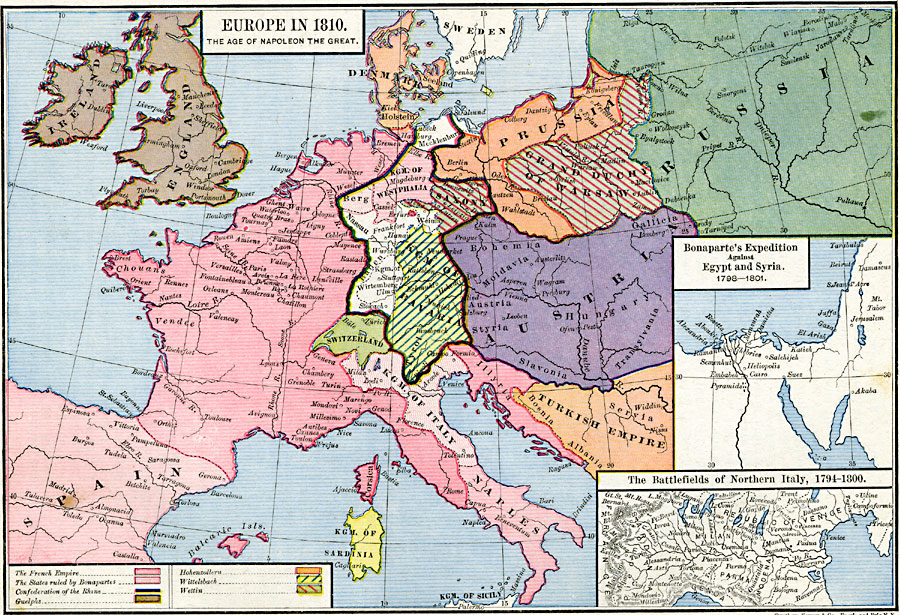
The year 1810 marks a pivotal moment in European history. The Napoleonic Wars were in full swing, reshaping the political landscape of the continent and leaving a lasting impact on its borders and social structures. Examining a map of Europe from this era provides a window into a tumultuous period, revealing the intricate web of alliances, conflicts, and societal shifts that defined the early 19th century.
The Napoleonic Shadow: A New Order Emerges
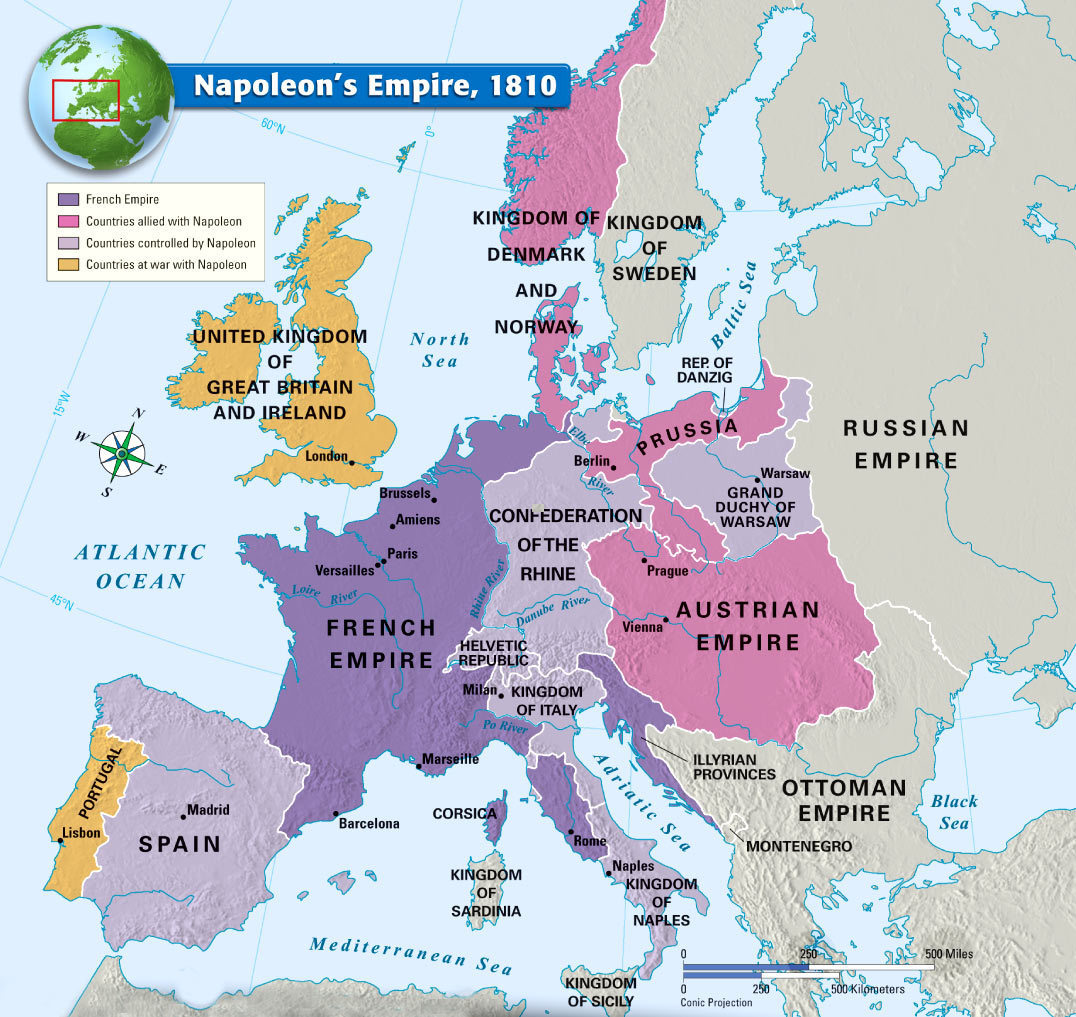
The map of Europe in 1810 is dominated by the presence of the French Empire, a testament to Napoleon Bonaparte’s relentless ambition and military prowess. After a series of victories, Napoleon had expanded his empire beyond France, incorporating territories like the Netherlands, Belgium, Italy, and parts of Spain and Germany. These newly acquired regions were integrated into the French system, subject to Napoleonic laws and administration.
A Shifting Mosaic of Power
Beyond the French Empire, the map reveals a fragmented Europe. The Holy Roman Empire, a loose federation of German states, had been dissolved in 1806, leaving a power vacuum in central Europe. The Austrian Empire, weakened by defeat, struggled to maintain its influence. The Kingdom of Prussia, once a formidable power, had been humbled by Napoleon and was relegated to the periphery of European politics.
The Rise of New Kingdoms and Empires
The Napoleonic Wars also witnessed the emergence of new kingdoms and empires. The Kingdom of Spain, embroiled in a brutal civil war, was effectively ruled by Napoleon’s brother Joseph. The Kingdom of Italy, established under Napoleon’s control, encompassed much of the Italian peninsula. In the east, the Russian Empire, under Tsar Alexander I, emerged as a significant force, its vast territory extending across Eastern Europe and into Asia.
The Impact of the Napoleonic Wars
The map of Europe in 1810 reflects the profound impact of the Napoleonic Wars. The wars had brought widespread destruction and upheaval, forcing millions to flee their homes and leaving economies in ruins. However, they also fostered a sense of nationalism and a desire for political change. The French Revolution, which had inspired Napoleon’s rise, had sown the seeds of liberal ideas, challenging traditional monarchies and sparking calls for greater political participation.
A Precursor to Change: The Seeds of Modern Europe
The map of Europe in 1810 provides a snapshot of a continent in transition. The Napoleonic Wars, though devastating, ultimately contributed to the emergence of a new European order. The Congress of Vienna, convened in 1814-1815, aimed to restore stability and balance to the continent, but it could not erase the profound changes that had been wrought by the Napoleonic era. The map of Europe in 1810, therefore, serves as a reminder of the transformative power of war and the enduring legacy of Napoleon’s ambition.
Understanding the Map: Key Features and Interpretations
To fully appreciate the significance of the map of Europe in 1810, it is essential to understand its key features and interpret its nuances. Here are some key aspects to consider:
-
Political Boundaries: The map clearly outlines the boundaries of the major empires, kingdoms, and states that existed in Europe at the time. It highlights the expansion of the French Empire and the fragmentation of other major powers.
-
Territorial Disputes: The map also reveals areas of territorial dispute and conflict. The ongoing wars between France and its enemies, including Britain, Russia, Austria, and Prussia, are evident in the contested territories.
-
Cultural and Linguistic Diversity: The map reflects the diverse cultural and linguistic landscape of Europe. It shows the presence of different languages, religions, and cultural traditions, highlighting the complexity of European society.
-
Economic Networks: The map can also be used to understand the economic networks of Europe at the time. Trade routes, major cities, and industrial centers are important elements to consider.
-
Historical Context: The map of Europe in 1810 should be interpreted within its historical context. Understanding the events leading up to this period, including the French Revolution and the rise of Napoleon, is crucial to fully appreciate the significance of the map.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Map
1. What was the impact of the Napoleonic Wars on the map of Europe?
The Napoleonic Wars drastically altered the map of Europe, leading to the expansion of the French Empire, the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, and the emergence of new kingdoms and empires. The wars also triggered a period of political instability and territorial disputes, ultimately shaping the geopolitical landscape of the continent for decades to come.
2. Why was the map of Europe in 1810 considered a pivotal moment in history?
The map of Europe in 1810 marked a turning point in European history, reflecting the culmination of the Napoleonic Wars and the rise of a new European order. The wars had fundamentally transformed the political, social, and economic fabric of the continent, leaving an indelible mark on the map and its future.
3. What were the major powers in Europe in 1810?
The major powers in Europe in 1810 included the French Empire, the Austrian Empire, the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the United Kingdom. These powers were engaged in a complex web of alliances and conflicts, shaping the destiny of the continent.
4. How did the map of Europe in 1810 influence the future of the continent?
The map of Europe in 1810 served as a foundation for the future of the continent. The Congress of Vienna, convened after the Napoleonic Wars, aimed to restore stability and order to Europe, but it could not erase the profound changes that had taken place. The map of 1810, therefore, laid the groundwork for the emergence of new political structures, national identities, and economic systems that would shape the course of European history for centuries to come.
Tips for Exploring the Map of Europe in 1810
-
Use Historical Atlases: Consult historical atlases and maps to gain a deeper understanding of the political boundaries, territorial disputes, and major cities of Europe in 1810.
-
Research Primary Sources: Explore primary sources, such as letters, diaries, and official documents, to gain insights into the experiences of people living in Europe during this period.
-
Analyze Historical Data: Use historical data, such as population statistics, trade records, and military records, to understand the social, economic, and political dynamics of the era.
-
Engage with Secondary Sources: Read scholarly articles and books on the Napoleonic Wars, the Congress of Vienna, and the history of Europe in the early 19th century to gain a comprehensive understanding of the context surrounding the map of Europe in 1810.
-
Visualize the Map: Create your own visualizations of the map of Europe in 1810, using software or online tools, to better understand its key features and interpret its significance.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Change and Transformation
The map of Europe in 1810 is more than just a collection of lines and borders. It is a testament to the dynamism and complexity of European history, reflecting the interplay of power, ambition, and societal change. By studying this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the tumultuous events that shaped the continent and the enduring legacy of the Napoleonic era. It serves as a reminder that the map of Europe, like the continent itself, is constantly evolving, shaped by the forces of history, politics, and human endeavor.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Map of Europe in 1810. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!