Deciphering Colorado’s Precipitation Patterns: A Guide To The State’s Vital Water Cycle
Deciphering Colorado’s Precipitation Patterns: A Guide to the State’s Vital Water Cycle
Related Articles: Deciphering Colorado’s Precipitation Patterns: A Guide to the State’s Vital Water Cycle
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering Colorado’s Precipitation Patterns: A Guide to the State’s Vital Water Cycle. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering Colorado’s Precipitation Patterns: A Guide to the State’s Vital Water Cycle

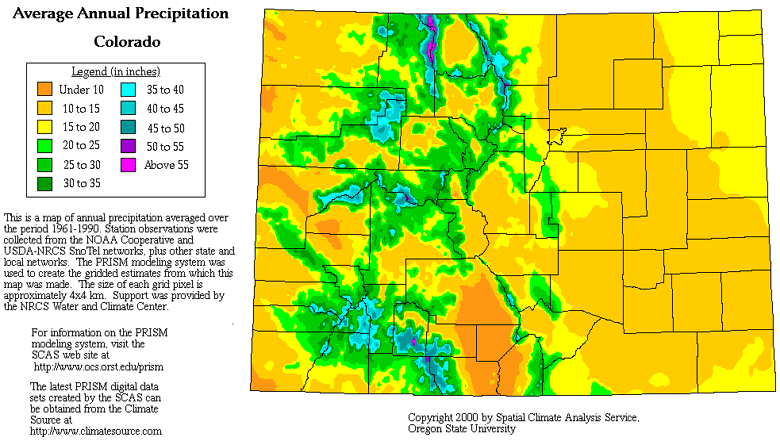
Colorado, known for its majestic mountains, vibrant landscapes, and diverse ecosystems, experiences a fascinating array of precipitation patterns. Understanding these patterns is crucial for managing water resources, predicting natural hazards, and appreciating the intricate balance of the state’s environment. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Colorado’s precipitation map, providing insights into its key features, influencing factors, and implications for various aspects of the state’s life.
Understanding the Basics: Precipitation in Colorado
Precipitation, the lifeline of any ecosystem, encompasses all forms of water falling from the atmosphere to the earth’s surface. In Colorado, this includes rain, snow, hail, sleet, and even fog. The distribution of precipitation across the state is highly variable, driven by a complex interplay of geographical features, atmospheric conditions, and seasonal fluctuations.
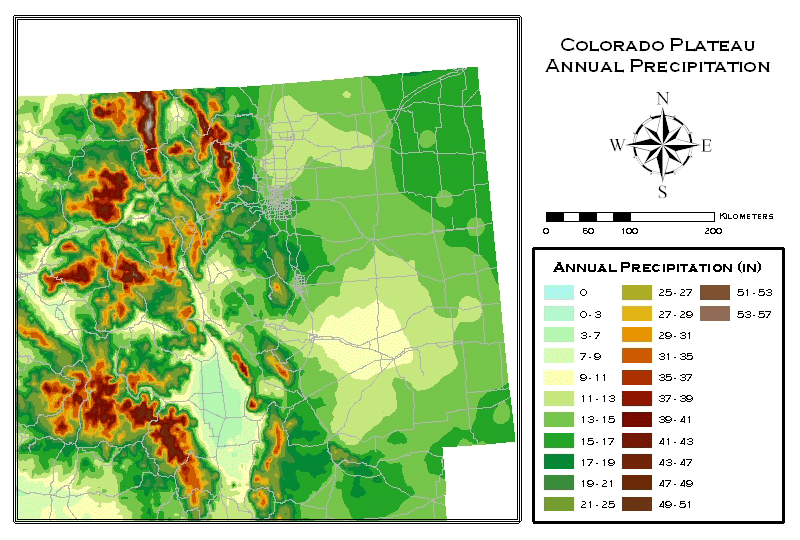
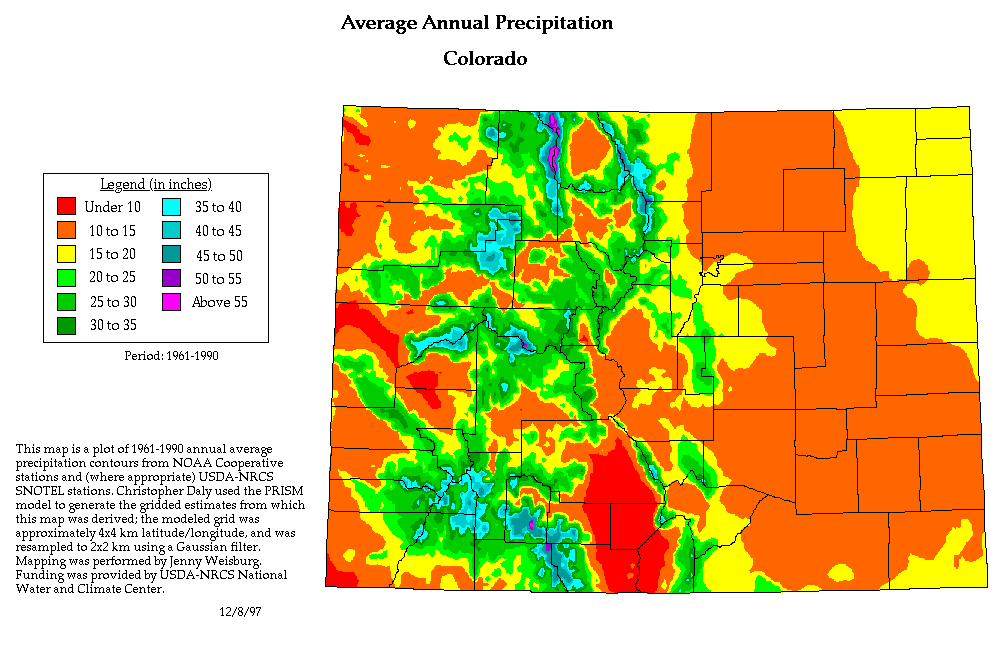
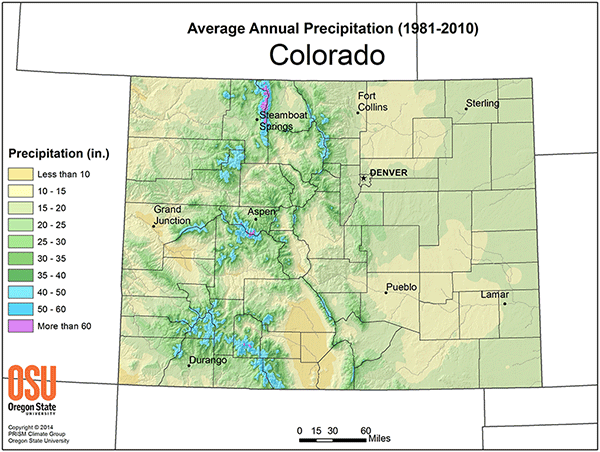
Key Features of the Colorado Precipitation Map
The Colorado precipitation map vividly illustrates the diverse patterns of rainfall and snowfall across the state. Here are some of its key features:
- Orographic Lifting: Mountains play a pivotal role in shaping Colorado’s precipitation. As air masses rise over the elevated terrain, they cool, leading to condensation and precipitation. The western slopes of the Rockies, particularly in the higher elevations, receive significantly more precipitation than the eastern plains.
- Elevation Gradient: Precipitation generally decreases with altitude. Higher elevations experience colder temperatures, favoring snowfall over rain. This pattern is evident in the snow-capped peaks of the Rocky Mountains, which contrast with the drier conditions on the eastern plains.
- Seasonal Variations: Precipitation patterns in Colorado exhibit distinct seasonal variations. The spring and summer months typically see higher rainfall, with thunderstorms and occasional heavy downpours. Winter brings significant snowfall, particularly in the mountainous regions.
- Regional Differences: Different regions of Colorado experience varying levels of precipitation. The Western Slope, influenced by the Pacific Ocean, receives higher rainfall than the Eastern Slope, which is more arid. The Front Range, situated between the mountains and plains, experiences a mix of rainfall and snowfall.
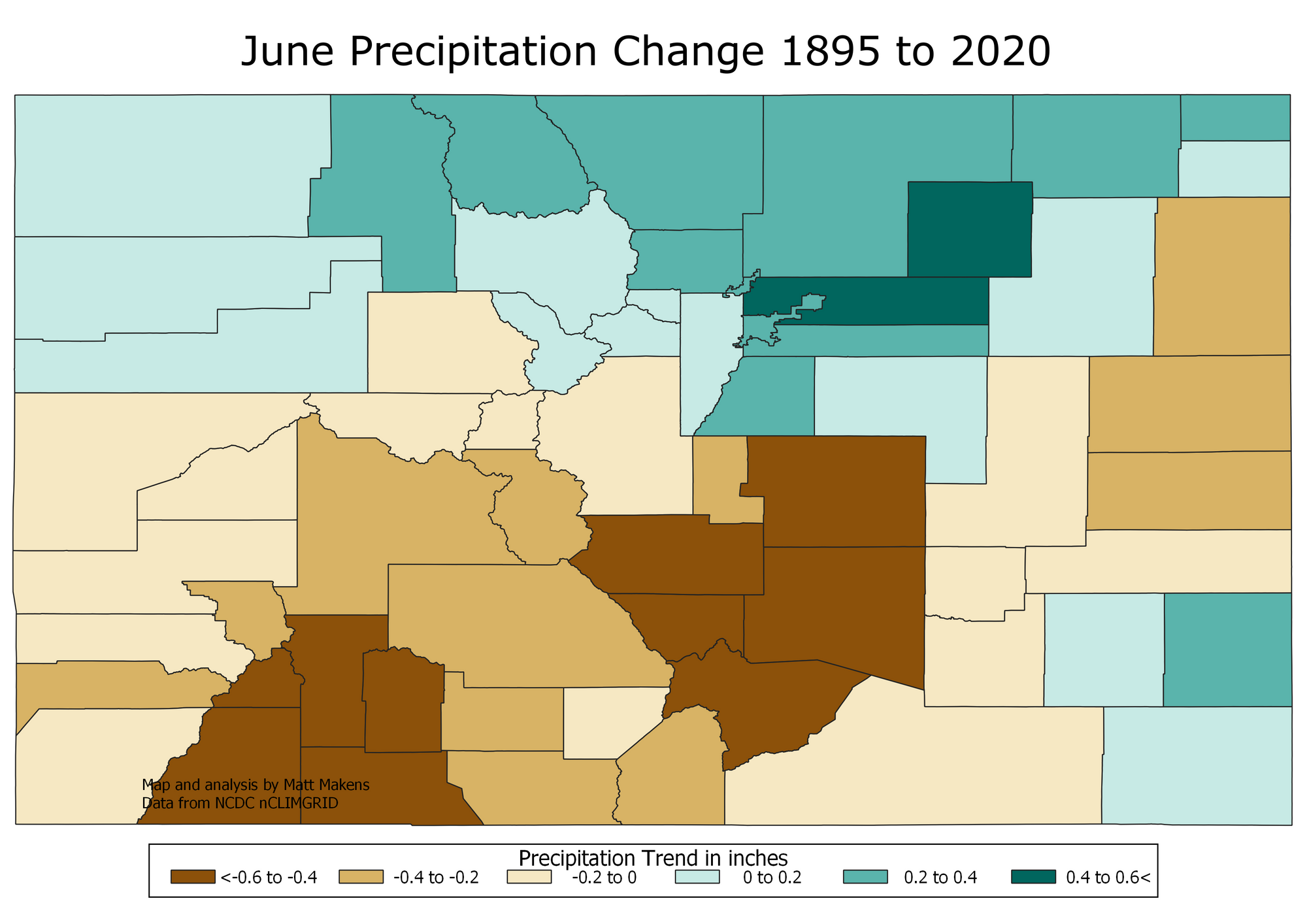
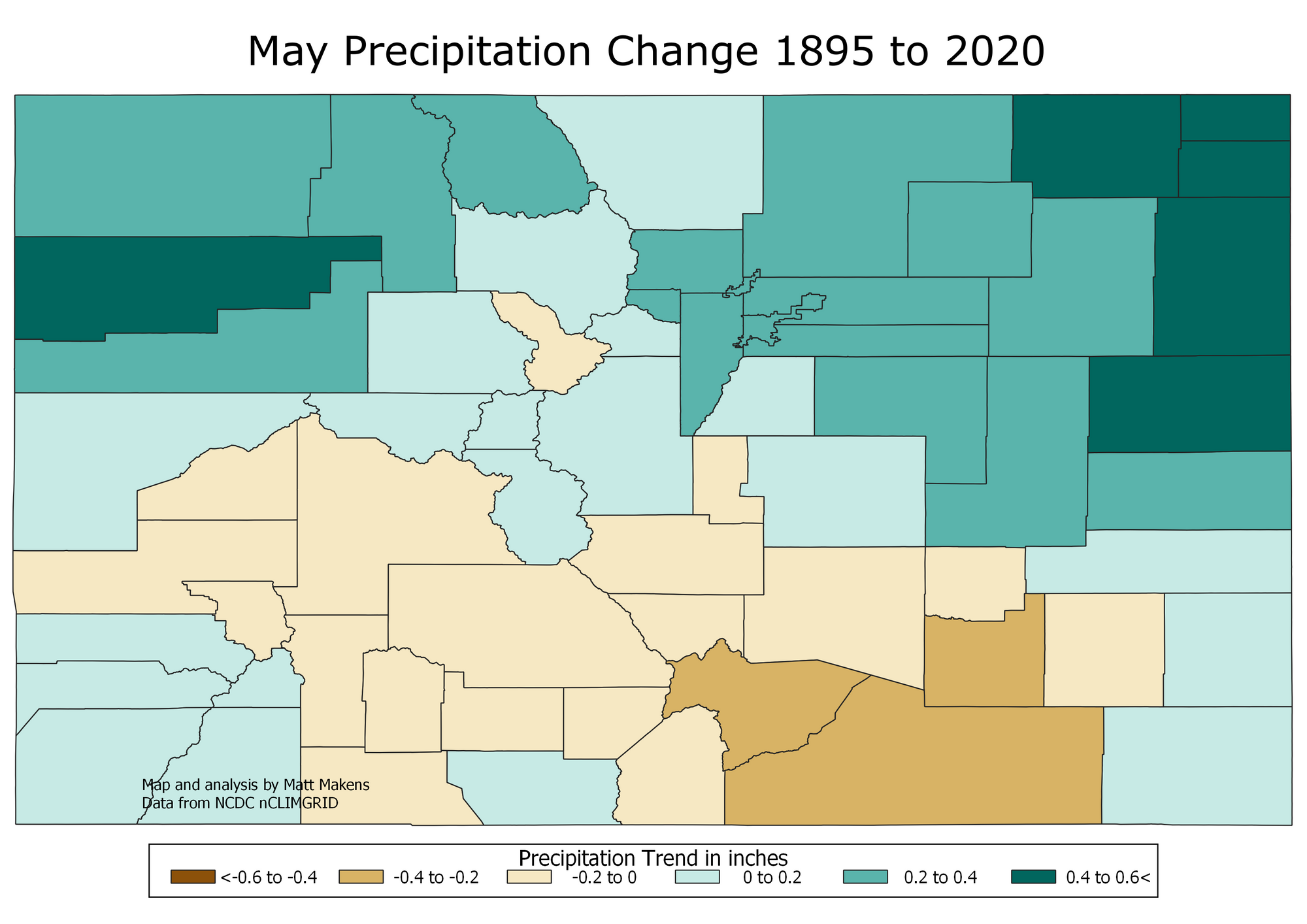
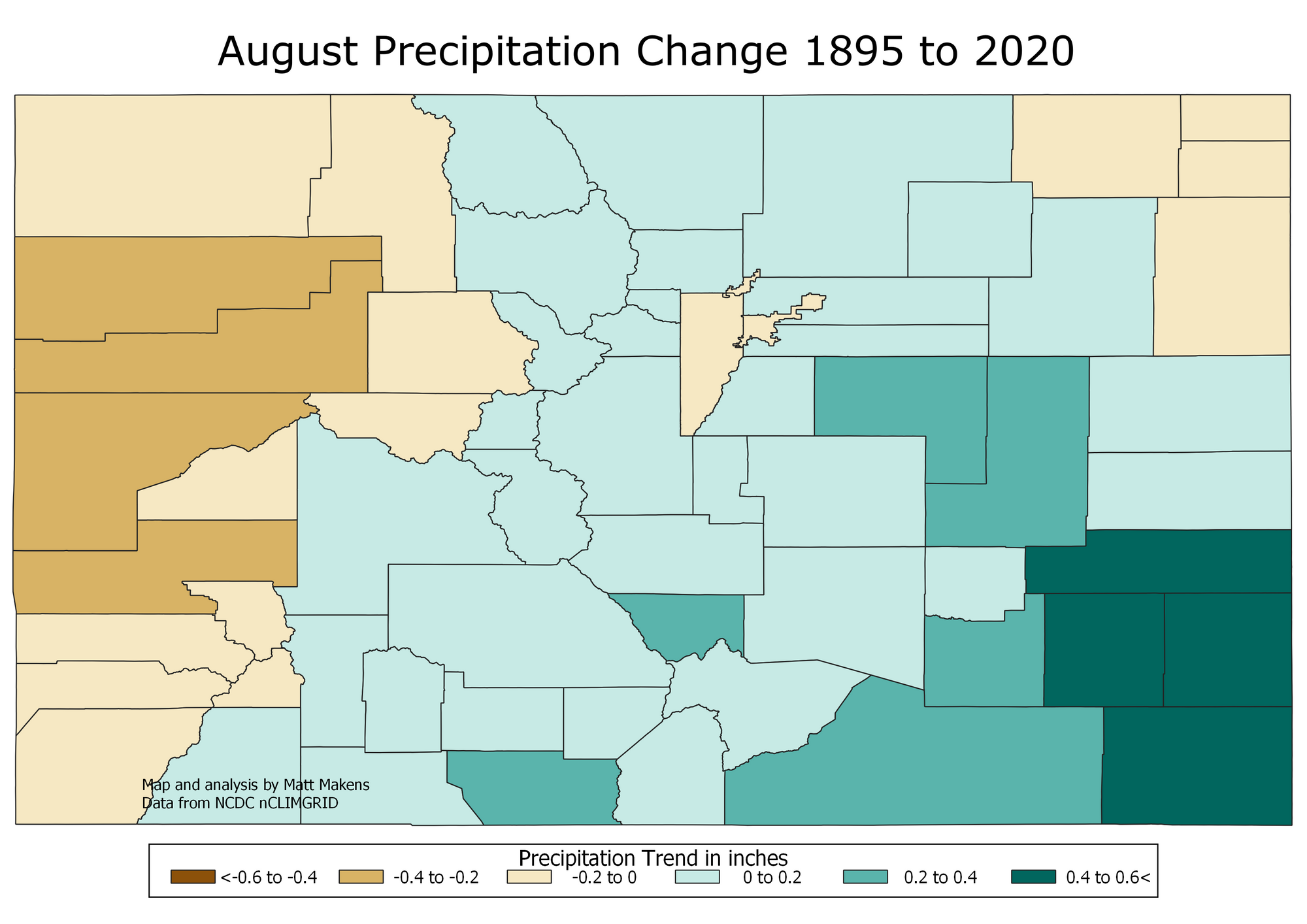
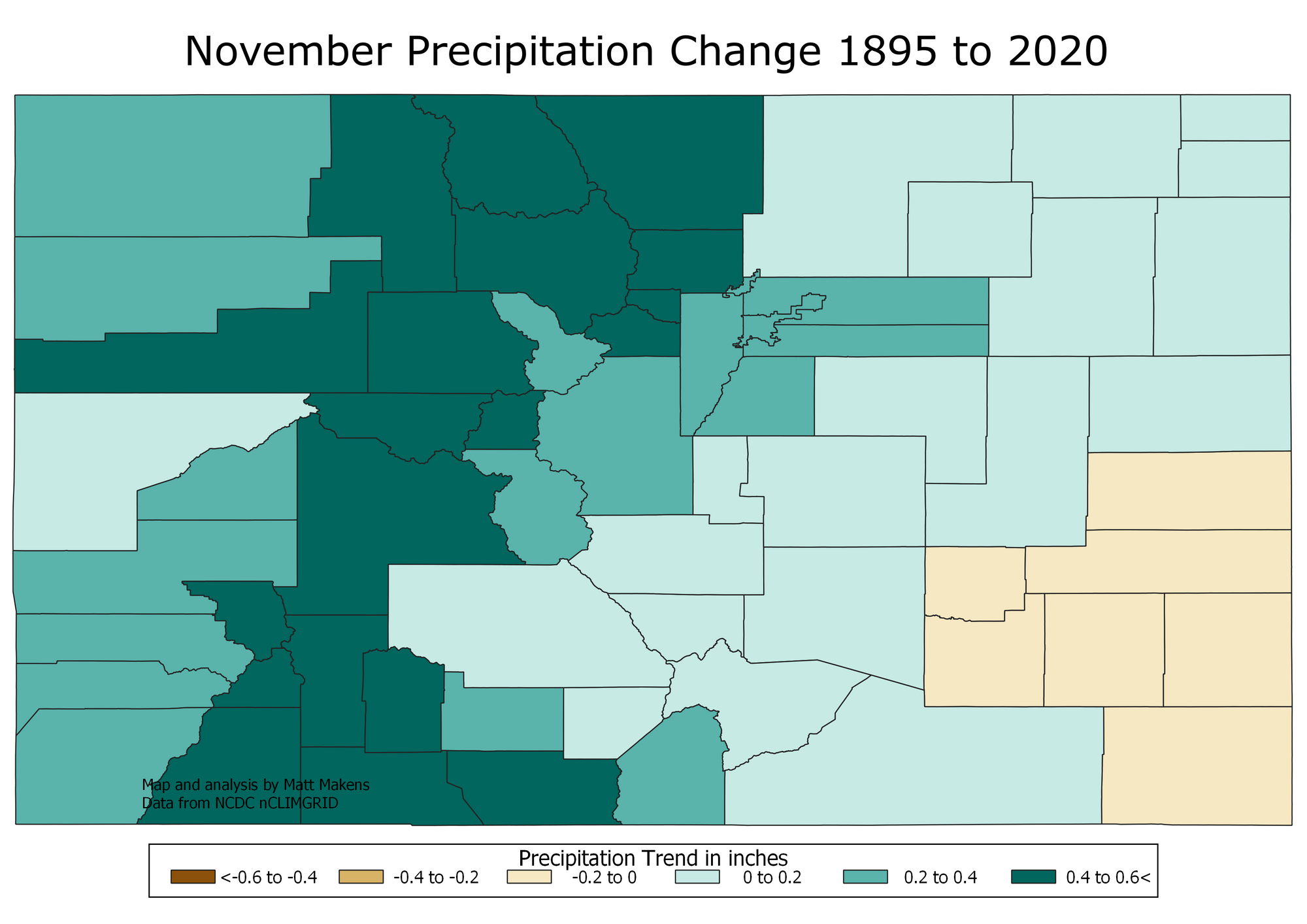
- Climate Change Impacts: The influence of climate change on precipitation patterns is becoming increasingly apparent. Warmer temperatures are leading to more evaporation, potentially impacting snowpack and altering the timing of precipitation events.
Factors Influencing Precipitation Patterns
Several factors interact to shape the intricate precipitation patterns observed in Colorado:
- Latitude: Colorado’s location between 37° and 41° north latitude influences its climate. The state experiences a semi-arid climate with distinct seasonal variations.
- Altitude: The state’s mountainous terrain creates significant elevation differences, leading to variations in temperature and precipitation.
- Wind Patterns: Prevailing winds, such as the westerly winds from the Pacific Ocean, carry moisture into the state, influencing precipitation patterns.
- Atmospheric Pressure Systems: Low-pressure systems often bring storms and precipitation, while high-pressure systems tend to be associated with dry conditions.
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO): This climate pattern can influence precipitation in Colorado. El Niño years are often associated with increased precipitation, while La Niña years tend to be drier.
The Significance of the Precipitation Map
Understanding the intricacies of the Colorado precipitation map is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Water Resource Management: Precipitation is the primary source of water for Colorado’s rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. The map helps water managers assess water availability, plan irrigation systems, and ensure sustainable water use.
- Agriculture and Ranching: Precipitation is essential for agriculture and ranching, impacting crop yields and livestock grazing. Farmers and ranchers rely on the map to plan planting schedules, manage water resources, and anticipate potential drought conditions.
- Natural Hazard Mitigation: Heavy precipitation can lead to flooding, landslides, and other natural hazards. The map helps identify areas at higher risk and inform mitigation strategies.
- Ecosystem Health: Precipitation plays a vital role in maintaining the health of Colorado’s diverse ecosystems, from alpine meadows to grasslands to forests. The map helps scientists understand how precipitation patterns influence plant and animal communities.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The map is essential for understanding how climate change is impacting precipitation patterns and for developing adaptation strategies to mitigate potential risks.
FAQs Regarding the Colorado Precipitation Map
Q: What is the average annual precipitation for Colorado?
A: The average annual precipitation for Colorado is approximately 18 inches (457 mm). However, this varies significantly across different regions, with the Western Slope receiving considerably more precipitation than the Eastern Slope.
Q: How does the precipitation map help predict floods?
A: The map helps identify areas prone to flooding by showing regions that receive high levels of precipitation, particularly during spring snowmelt or intense thunderstorms.
Q: Can the precipitation map be used to track drought conditions?
A: Yes, the map can be used to track drought conditions by comparing current precipitation levels to historical averages. Persistent below-average precipitation can indicate drought conditions.
Q: How does climate change affect the Colorado precipitation map?
A: Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, leading to changes in the frequency, intensity, and timing of precipitation events. Warmer temperatures can increase evaporation, potentially reducing snowpack and altering the timing of spring snowmelt.
Tips for Using the Colorado Precipitation Map
- Consult reliable sources: Use maps from reputable organizations like the National Weather Service or the Colorado Climate Center.
- Consider the time scale: Precipitation patterns can vary significantly over different time scales, from daily to seasonal to long-term trends.
- Analyze regional differences: Understand the distinct precipitation patterns across different regions of Colorado.
- Stay informed about current conditions: Monitor weather forecasts and precipitation updates to stay informed about current conditions.
- Integrate the map with other data sources: Combine precipitation data with other relevant information, such as soil moisture, streamflow, and vegetation conditions.
Conclusion
The Colorado precipitation map is a powerful tool for understanding the state’s complex and dynamic water cycle. By analyzing precipitation patterns, we can gain valuable insights into water resource management, natural hazard mitigation, ecosystem health, and the impacts of climate change. As we continue to navigate the challenges of a changing climate, the importance of understanding and interpreting precipitation data will only grow.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering Colorado’s Precipitation Patterns: A Guide to the State’s Vital Water Cycle. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!