Mapping The Roaring Heart Of The Wild: A Comprehensive Guide To Tiger Habitats
Mapping the Roaring Heart of the Wild: A Comprehensive Guide to Tiger Habitats
Related Articles: Mapping the Roaring Heart of the Wild: A Comprehensive Guide to Tiger Habitats
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Roaring Heart of the Wild: A Comprehensive Guide to Tiger Habitats. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Roaring Heart of the Wild: A Comprehensive Guide to Tiger Habitats

The tiger, a majestic predator and apex predator, is a symbol of strength, beauty, and wildness. Its presence in a landscape signifies a healthy ecosystem, one teeming with life. But the tiger’s future is precarious, facing threats from habitat loss, poaching, and human encroachment. Understanding where tigers live is crucial for their conservation and ensuring their continued existence.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of tiger habitats, exploring the geographical distribution, ecological factors, and conservation challenges these magnificent animals face.
The Geographical Distribution of Tigers: A Tapestry of Stripes Across the World
Tigers are found in a diverse range of habitats across Asia, from the dense jungles of India to the snow-capped mountains of Siberia. Their distribution encompasses a vast area, spanning several countries and biomes. The map of tiger habitats is a testament to their adaptability and resilience.
1. The Indian Subcontinent: A Tiger Heartland
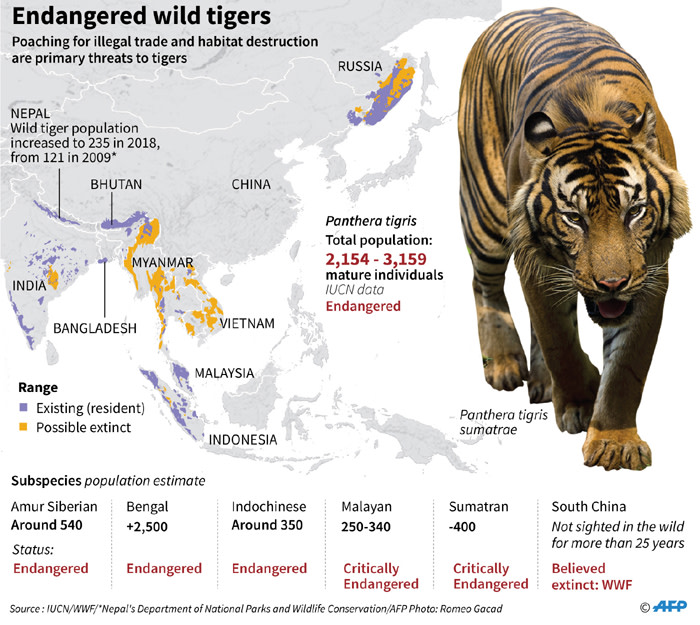
The Indian subcontinent is considered the heartland of tiger conservation. It is home to the largest tiger population in the world, with India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka harboring significant populations.
- India: With a wide range of habitats, from the lush forests of the Western Ghats to the dry deciduous forests of central India, India holds the highest number of tigers in the world.
- Nepal: The Terai region of Nepal, bordering India, is a crucial habitat for tigers, known for its dense forests and abundant prey.
- Bhutan: The high-altitude forests of Bhutan provide a sanctuary for tigers, particularly in the Manas National Park, which shares a border with India.
- Bangladesh: The Sundarbans mangrove forest, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is home to a unique population of Royal Bengal tigers adapted to the brackish water environment.
- Sri Lanka: The island nation of Sri Lanka boasts a smaller tiger population, primarily found in the Wilpattu National Park, a sprawling dry zone forest.
2. Southeast Asia: A Mosaic of Habitats
Southeast Asia harbors a diverse range of tiger subspecies, each adapted to its specific environment.
- Indonesia: The islands of Sumatra and Borneo are home to the Sumatran tiger and the critically endangered Sumatran tiger, respectively.
- Malaysia: The Malay Peninsula is home to the Malayan tiger, a subspecies known for its distinctive dark stripes.
- Thailand: Thailand’s national animal, the Indochinese tiger, is found in the dense forests of the country’s western and southern regions.
- Myanmar: Myanmar’s forests, particularly in the Tanintharyi region, provide habitat for the Indochinese tiger and the endangered Bengal tiger.
- Vietnam: Vietnam’s forests, particularly the Vu Quang National Park, are home to a small population of Indochinese tigers.
- Cambodia: Cambodia’s forests, particularly the Cardamom Mountains, harbor a small population of Indochinese tigers.
- Laos: Laos’ forests, particularly the Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area, are home to a small population of Indochinese tigers.
3. Eastern Russia: The Siberian Tiger’s Domain
The Siberian tiger, the largest cat in the world, is found in the remote and unforgiving forests of eastern Russia.
- Russia: The Russian Far East, particularly the Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsk Krai regions, are home to the Siberian tiger, which thrives in the boreal forests and mountainous terrain.
4. China: A Fragmented Landscape
China’s tiger population has been significantly reduced due to habitat loss and poaching. However, there are ongoing efforts to reintroduce tigers into protected areas.
- China: The South China tiger, once found in southern China, is now critically endangered and possibly extinct in the wild. However, there are ongoing efforts to reintroduce tigers into protected areas.
Understanding the Ecology of Tiger Habitats: A Complex Web of Life
Tigers are apex predators, playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. Their presence indicates a healthy and diverse food web.
1. Prey Abundance: The Foundation of a Tiger’s Realm
Tigers rely on a variety of prey species, including deer, wild pigs, and other ungulates. The abundance and distribution of prey are crucial factors influencing tiger density and survival.
2. Forest Cover: A Sanctuary for the Striped King
Tigers require extensive forest cover for shelter, hunting, and raising their cubs. Dense forests provide protection from predators and humans, ensuring a safe haven for tigers.
3. Water Sources: Lifeblood of the Jungle
Access to water sources is essential for tigers, especially during the dry season. Waterholes and rivers serve as drinking spots and hunting grounds.
4. Landscape Connectivity: Linking Tiger Territories
Maintaining connectivity between tiger habitats is crucial for gene flow and dispersal. Corridors and protected areas help connect isolated populations, reducing the risk of inbreeding and extinction.
5. Human Impact: A Growing Threat
Human activities, such as deforestation, poaching, and habitat fragmentation, pose significant threats to tiger populations. These activities disrupt the delicate balance of tiger ecosystems, leading to habitat loss, prey depletion, and human-wildlife conflict.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts: Protecting the Tiger’s Future
The future of tigers hangs in the balance. The challenges they face are multifaceted, requiring a collaborative approach to conservation.
1. Habitat Loss: A Shrinking Sanctuary
Habitat loss is the most significant threat to tigers. Deforestation for agriculture, logging, and infrastructure development has fragmented tiger habitats, reducing their range and prey availability.
2. Poaching: A Grim Reality
Poaching for tiger parts, particularly for traditional medicine, has driven tiger populations to the brink of extinction. The illegal wildlife trade remains a significant threat, despite international efforts to combat it.
3. Human-Wildlife Conflict: A Growing Tension
As human populations expand, encroachment into tiger habitats is increasing, leading to conflicts between humans and tigers. This conflict often results in retaliatory killings of tigers, further jeopardizing their survival.
4. Climate Change: An Emerging Threat
Climate change is expected to exacerbate existing threats to tigers, including habitat loss, prey depletion, and increased human-wildlife conflict. Rising temperatures and changes in rainfall patterns could disrupt ecosystems, making it harder for tigers to survive.
Conservation Efforts: A Multi-Pronged Approach
Conservation efforts are essential for the survival of tigers. These efforts involve a range of strategies, from habitat protection to community engagement.
1. Protected Areas: Safe Havens for Tigers
Establishing and managing protected areas is crucial for safeguarding tiger populations. These areas provide safe havens for tigers, protecting them from poaching and habitat loss.
2. Anti-Poaching Patrols: Guardians of the Wild
Anti-poaching patrols are essential for deterring poachers and protecting tigers. These patrols monitor tiger habitats, apprehend poachers, and educate local communities about the importance of tiger conservation.
3. Community Engagement: Building Partnerships
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for long-term success. This involves educating communities about the value of tigers, providing alternative livelihoods, and addressing human-wildlife conflict.
4. Research and Monitoring: Tracking the Stripes
Research and monitoring are essential for understanding tiger populations, their habitat requirements, and the effectiveness of conservation efforts. This involves tracking tiger movements, assessing prey abundance, and monitoring habitat conditions.
5. International Cooperation: A Global Effort
International cooperation is essential for addressing the transnational nature of the tiger trade and habitat loss. Governments, conservation organizations, and local communities must work together to protect tigers and their habitats.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Tiger Habitats
1. What are the main threats to tiger populations?
The main threats to tiger populations include habitat loss, poaching, human-wildlife conflict, and climate change.
2. Why is it important to conserve tigers?
Tigers play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. They are apex predators, regulating prey populations and ensuring a healthy food web. Their presence indicates a healthy and thriving ecosystem.
3. How can I help conserve tigers?
You can help conserve tigers by supporting conservation organizations, raising awareness about tiger conservation, and making sustainable choices that minimize your impact on the environment.
4. What are some of the key conservation efforts underway?
Key conservation efforts include establishing protected areas, conducting anti-poaching patrols, engaging local communities, conducting research and monitoring, and promoting international cooperation.
5. What is the future of tigers?
The future of tigers is uncertain. However, with continued conservation efforts, it is possible to ensure their survival and protect these magnificent animals for generations to come.
Tips for Understanding and Protecting Tiger Habitats
1. Educate Yourself: Learn about tiger habitats, their ecology, and the threats they face.
2. Support Conservation Organizations: Donate to organizations working to protect tigers and their habitats.
3. Choose Sustainable Products: Support businesses that are committed to sustainable practices, such as palm oil free products and responsibly sourced wood.
4. Reduce Your Carbon Footprint: Make changes in your lifestyle to reduce your environmental impact, such as reducing energy consumption and choosing sustainable transportation.
5. Advocate for Change: Speak out against poaching and habitat destruction, and encourage others to do the same.
Conclusion: A Roaring Call to Action
The map of tiger habitats is a testament to their resilience and adaptability. However, their future is uncertain. The challenges they face are complex and require a multi-pronged approach to conservation. By understanding the threats they face, supporting conservation efforts, and making sustainable choices, we can help ensure the survival of these magnificent creatures and protect the ecosystems they call home. The fate of the tiger rests in our hands.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Roaring Heart of the Wild: A Comprehensive Guide to Tiger Habitats. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!