Mapping the Third Crusade: A Journey Through History
Related Articles: Mapping the Third Crusade: A Journey Through History
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Third Crusade: A Journey Through History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Third Crusade: A Journey Through History
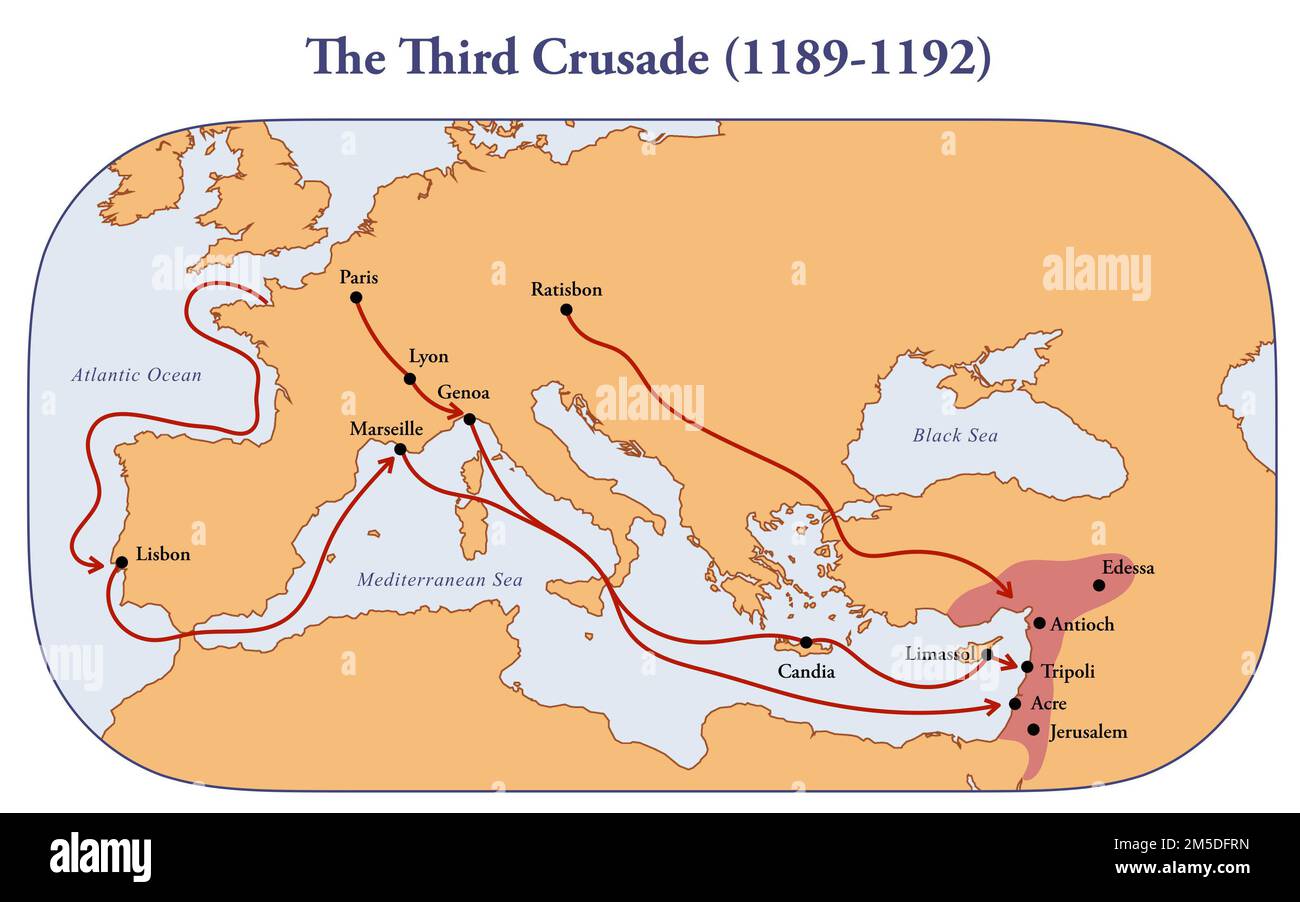
The Third Crusade, a pivotal moment in the history of the Crusades, saw a clash of empires and ideologies, leaving an enduring mark on the Middle East and Europe. Understanding the geography of this conflict is essential for comprehending its complexities and significance. This article delves into the map of the Third Crusade, examining its routes, key locations, and strategic importance, while exploring its lasting impact on the world.
The Setting: A Clash of Worlds
The Third Crusade was a response to the capture of Jerusalem by Saladin, the powerful Ayyubid sultan, in 1187. The fall of the Holy City, a sacred site for both Christians and Muslims, ignited outrage across Europe, prompting King Philip II of France, King Richard I of England, and Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa to launch a crusade to reclaim it.
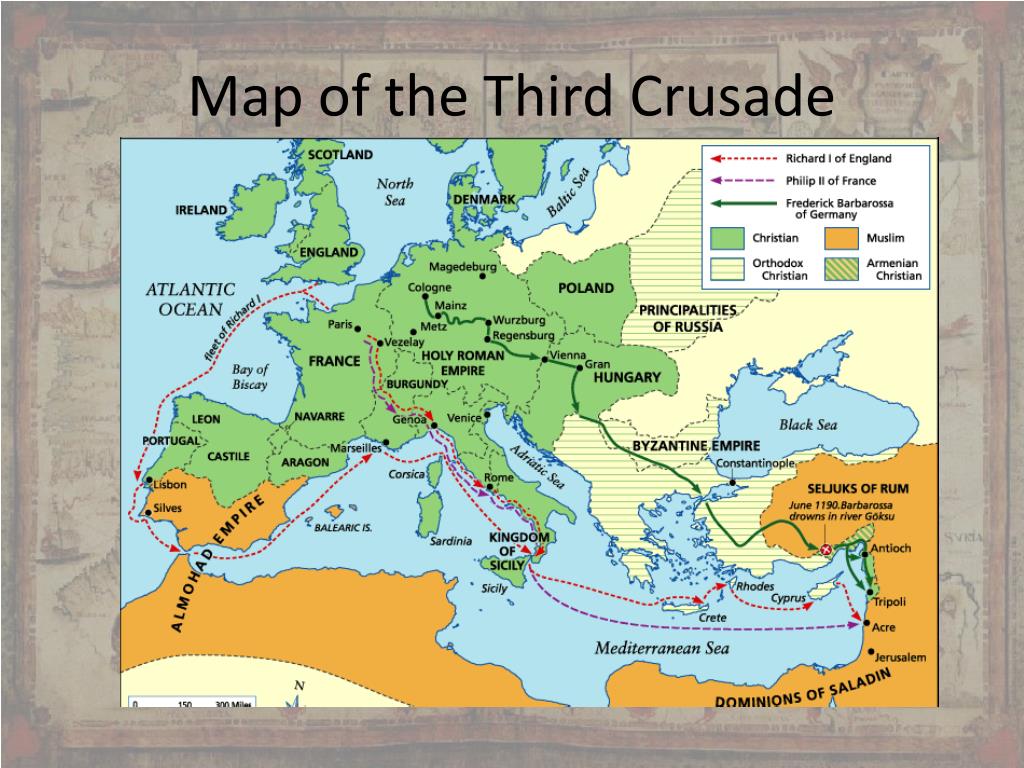
The Routes: A Complex Web of Movements
The map of the Third Crusade reveals a complex network of routes, each with its own challenges and strategic implications:
-
Frederick Barbarossa’s Route: The Holy Roman Emperor led his forces through the Byzantine Empire and into Anatolia, aiming to reach Jerusalem via the land route. However, he drowned in the Saleph River in 1190, leading to the disintegration of his army.
-
Philip II’s Route: The French king sailed directly to Acre, a vital port city on the Mediterranean coast, where he joined the siege already underway. He played a significant role in the capture of Acre but left the crusade in 1191, leaving Richard I as the sole leader.
-
Richard I’s Route: The English king embarked on a more ambitious journey, sailing to Acre after a brief stopover in Messina, Sicily. He led the siege of Acre, secured its capture, and launched a series of campaigns throughout the Levant, culminating in a series of battles and negotiations with Saladin.
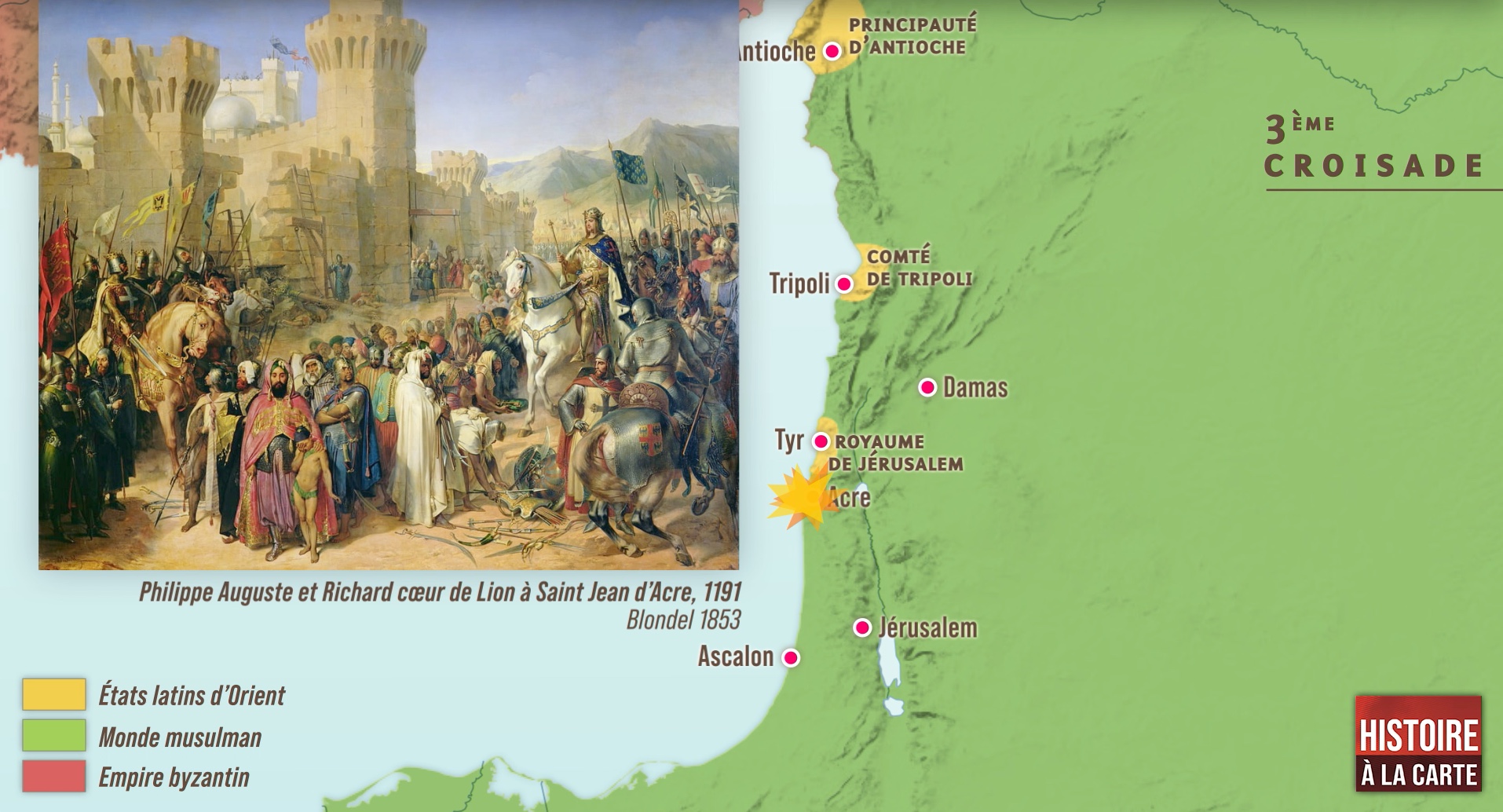
Key Locations: The Theaters of Conflict
The map of the Third Crusade highlights several key locations that served as battlegrounds and strategic hubs:
-
Acre: This fortified port city became the central focus of the crusade. Its capture in 1191 marked a major victory for the Crusaders but also came at a heavy cost.
-
Arsuf: This coastal plain witnessed a decisive battle in 1191, where Richard I’s forces defeated Saladin’s army, solidifying their control over the coastal region.
-
Jaffa: This port city, strategically located between Acre and Jerusalem, was captured by Richard I in 1192. It became a key base for the Crusaders and served as a launching point for further campaigns.
-
Jerusalem: The Holy City remained the ultimate goal of the Third Crusade. While Richard I failed to recapture it, he managed to secure a treaty with Saladin, granting Christian pilgrims access to the city.
Strategic Importance: A Battle for Control
The map of the Third Crusade underscores the strategic importance of the Levant, a region connecting Europe, Africa, and Asia. The Crusaders sought to control this vital trade route and secure access to the Holy Land, while Saladin aimed to defend his territory and maintain Muslim control over Jerusalem.
The Lasting Impact: A Shift in Power Dynamics
The Third Crusade, despite its mixed outcomes, had a lasting impact on the Middle East and Europe:
-
Weakening of the Crusader States: While the Crusaders secured some victories, their power in the Levant was weakened, leading to the decline of the Crusader states.
-
Rise of Saladin’s Influence: The Ayyubid sultan emerged as a powerful figure, consolidating his control over the region and establishing a strong Muslim presence.
-
Renewed Interest in the Holy Land: The Crusade reignited European interest in the Holy Land, leading to further crusades and the establishment of military orders like the Templars and Hospitallers.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Third Crusade
Q: What was the main objective of the Third Crusade?
A: The primary objective was to recapture Jerusalem from Saladin, who had taken it in 1187.
Q: Why was Acre so important?
A: Acre was a strategic port city on the Mediterranean coast, providing access to supplies and serving as a base for military operations.
Q: What was the outcome of the Third Crusade?
A: While Jerusalem was not recaptured, Richard I secured a treaty with Saladin, granting Christian pilgrims access to the city. The Crusade also led to the weakening of the Crusader states and the rise of Saladin’s influence.
Q: What were the major battles of the Third Crusade?
A: Key battles include the siege of Acre, the Battle of Arsuf, and the siege of Jaffa.
Q: How did the Third Crusade impact the Middle East?
A: It led to a shift in power dynamics, with Saladin emerging as a dominant figure and the Crusader states weakening. It also fueled further conflict and instability in the region.
Tips for Understanding the Map of the Third Crusade
-
Study the routes: Trace the movements of the Crusader armies and Saladin’s forces to understand their strategies and challenges.
-
Identify key locations: Focus on cities like Acre, Arsuf, and Jaffa to grasp the strategic importance of these locations.
-
Connect the map with historical events: Relate the map to key battles, sieges, and negotiations to understand their context and significance.
-
Consider the broader context: Examine the map within the larger framework of the Crusades and the political landscape of the time.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Conflict and Change
The map of the Third Crusade offers a visual representation of a complex and consequential conflict. It highlights the strategic importance of the Levant, the clash of ideologies, and the lasting impact of this historical event. By understanding the geography of the Third Crusade, we gain a deeper appreciation for its complexities and its enduring legacy on the world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Third Crusade: A Journey Through History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!