Navigating The Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Positioning Maps
Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Positioning Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Positioning Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Positioning Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Positioning Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Positioning Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of a Positioning Map
- 3.2 Benefits of Utilizing a Positioning Map
- 3.3 Key Components of a Positioning Map
- 3.4 Constructing a Positioning Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.5 Types of Positioning Maps
- 3.6 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.7 Tips for Effective Positioning Map Creation
- 3.8 Conclusion: Navigating the Competitive Landscape with Confidence
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Positioning Maps
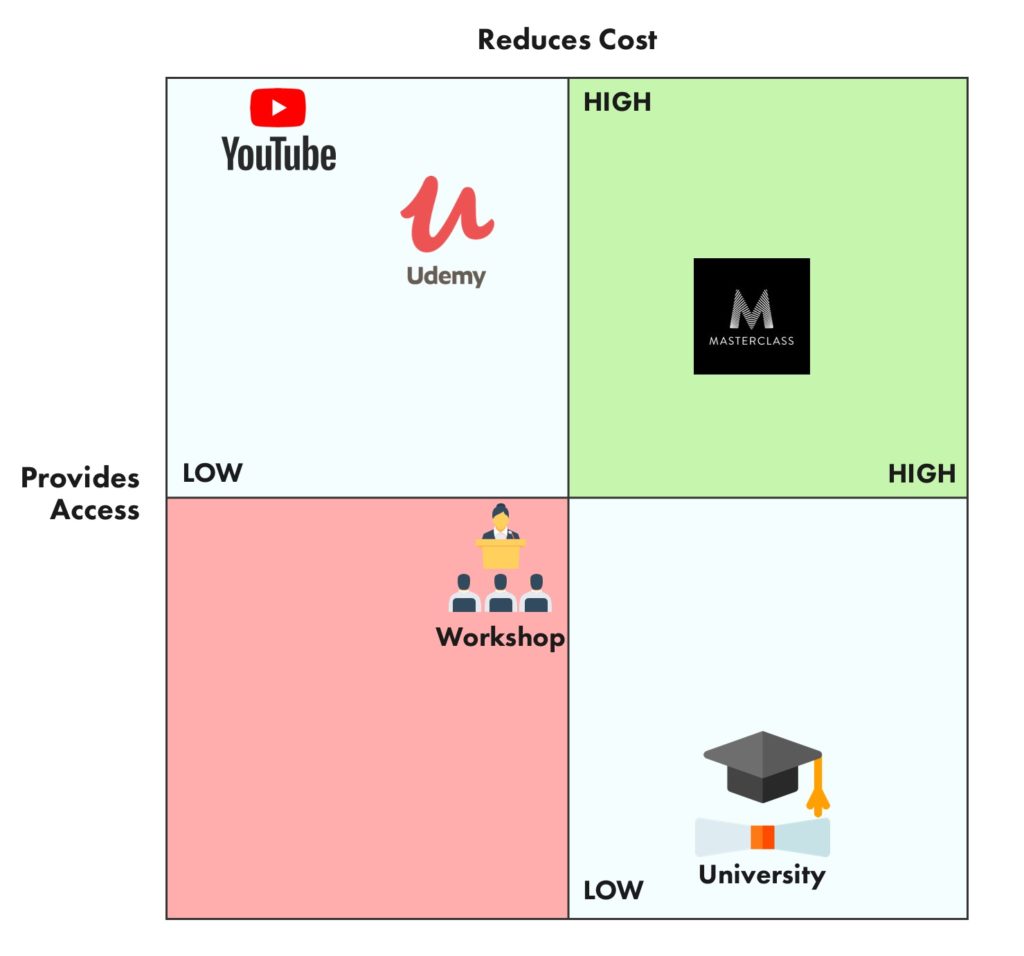
In the dynamic world of business, understanding your position within the market is crucial for success. A positioning map, also known as a perceptual map, is a powerful tool that helps businesses visualize their competitive landscape and identify opportunities for differentiation. This visual representation of how consumers perceive various brands within a specific industry allows for strategic decision-making, ensuring your brand stands out in a crowded marketplace.
Understanding the Essence of a Positioning Map
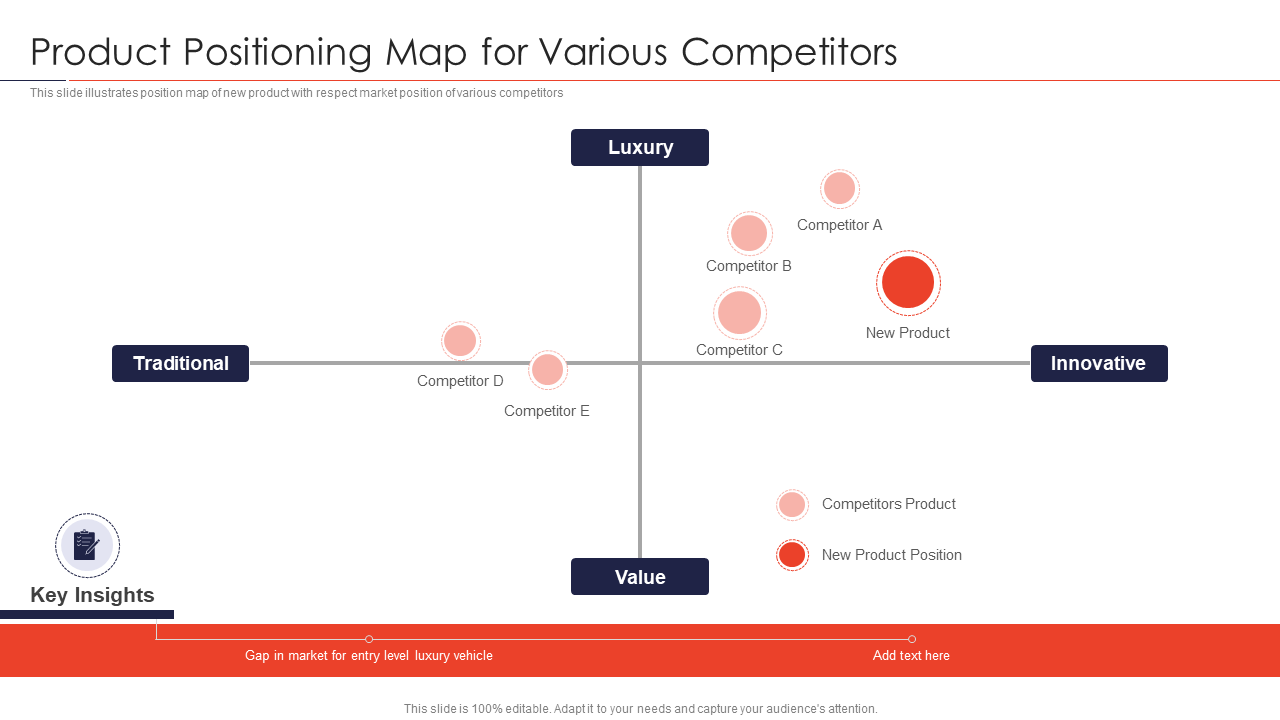
A positioning map is essentially a graphical representation of how consumers perceive different products or brands based on key attributes. It typically plots brands on a two-dimensional grid, with each axis representing a specific attribute or dimension. These attributes can range from price and quality to features and benefits, allowing businesses to analyze their position relative to competitors and understand consumer preferences.
Benefits of Utilizing a Positioning Map
The benefits of employing a positioning map are multifaceted, offering valuable insights that can significantly impact business strategy:
- Competitive Analysis: Positioning maps provide a clear visual representation of the competitive landscape, allowing businesses to identify direct competitors, assess their strengths and weaknesses, and understand their market share.
- Market Segmentation: By analyzing consumer perceptions, businesses can identify distinct market segments and tailor their marketing efforts to specific target audiences. This allows for more effective resource allocation and targeted messaging.
- Product Development: Understanding consumer preferences and competitor offerings through positioning maps can inform product development strategies. Businesses can identify gaps in the market, develop unique product features, and cater to specific consumer needs.
- Branding and Positioning: Positioning maps help businesses understand how their brand is perceived by consumers and identify opportunities for differentiation. By strategically positioning their brand on the map, businesses can create a unique value proposition and establish a strong brand identity.
- Marketing Strategy: Understanding consumer perceptions and competitive positioning allows for the development of targeted marketing campaigns. Positioning maps can guide messaging, channel selection, and overall marketing strategy to effectively reach the desired target audience.
Key Components of a Positioning Map
A well-constructed positioning map comprises several key components:
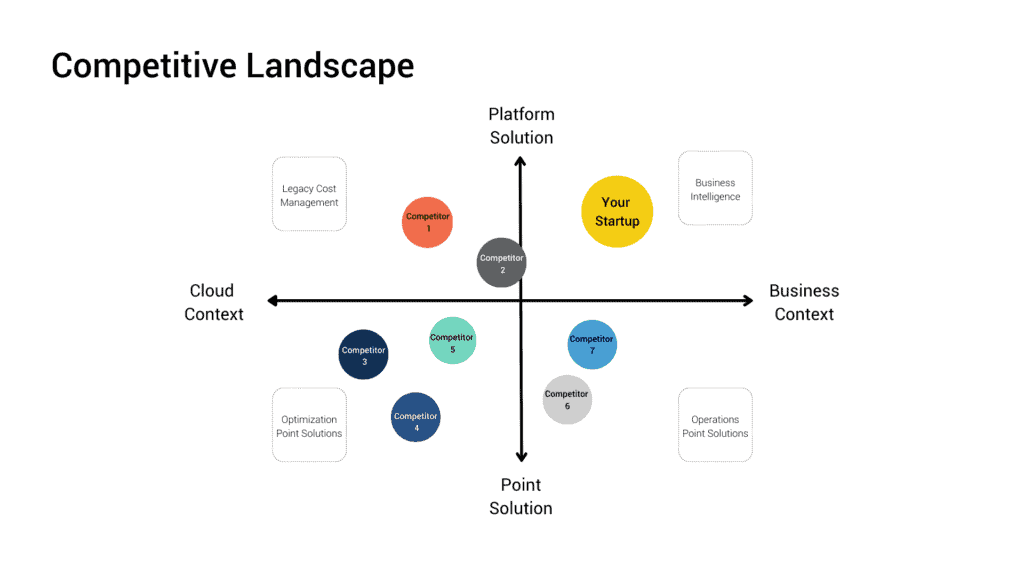
- Axes: These represent the key attributes or dimensions that define the market. Choosing the right axes is crucial for accurately reflecting consumer perceptions and competitive landscape.
- Brands: Each brand or product is plotted on the map based on its perceived position on the chosen axes. This allows for a visual comparison of different offerings and their relative positioning.
- Consumer Data: The data used to create the map should be based on consumer research, surveys, or market analysis. This ensures the map accurately reflects real-world perceptions and preferences.
- Gaps and Opportunities: By analyzing the map, businesses can identify gaps in the market, areas where competitors are lacking, and potential opportunities for differentiation.
- Positioning Statement: Based on the insights gained from the map, businesses can develop a clear and concise positioning statement that articulates their unique value proposition and target audience.
Constructing a Positioning Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating an effective positioning map requires a structured approach:
- Define the Market: Clearly define the industry or product category you are analyzing. This ensures that the map focuses on relevant competitors and consumer perceptions.
- Identify Key Attributes: Determine the most important attributes or dimensions that influence consumer choices within the defined market. These should be relevant, measurable, and easily understood by consumers.
- Gather Data: Collect data on consumer perceptions of different brands based on the chosen attributes. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or market research.
- Plot Brands: Based on the collected data, plot each brand or product on the map according to its perceived position on the chosen axes.
- Analyze and Interpret: Analyze the resulting map to identify key insights, such as market segments, competitive clusters, and potential opportunities for differentiation.
- Develop Positioning Statement: Based on the insights gained from the map, develop a clear and concise positioning statement that articulates your brand’s unique value proposition and target audience.
Types of Positioning Maps
There are various types of positioning maps, each offering a unique perspective on the competitive landscape:
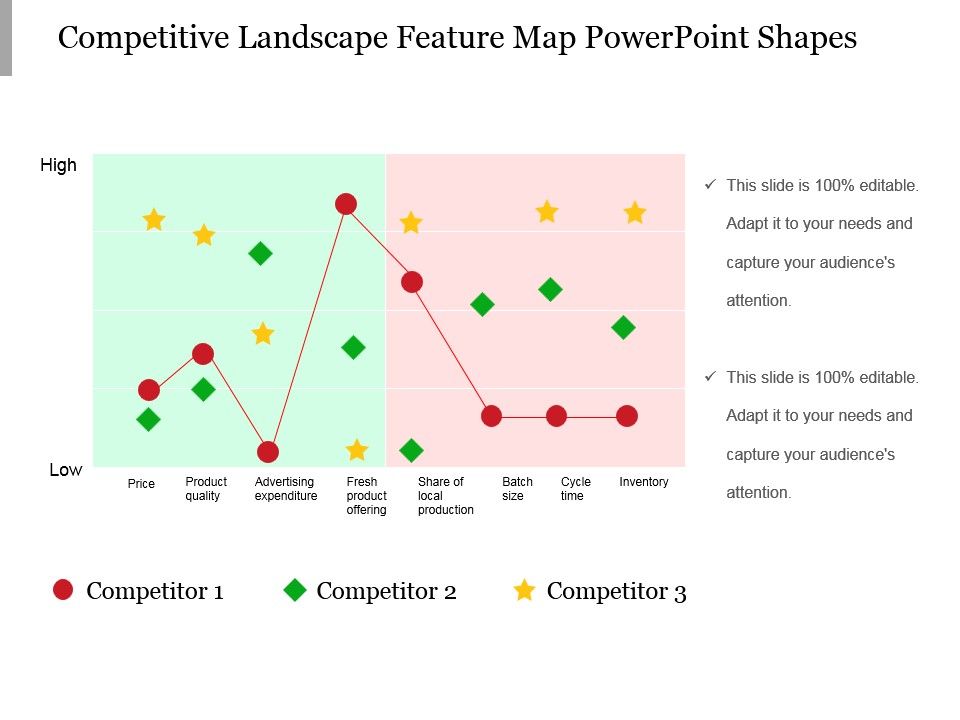
- Perceptual Maps: These maps focus on consumer perceptions of brands based on specific attributes, providing insights into how consumers differentiate between different offerings.
- Competitive Maps: These maps focus on the competitive landscape, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of competitors and their relative market share.
- Product Attribute Maps: These maps focus on specific product features and benefits, allowing businesses to understand how consumers value different attributes and identify opportunities for product development.
- Value Maps: These maps focus on the value proposition of different brands, allowing businesses to understand how consumers perceive the value they receive from each offering.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What data should I use to create a positioning map?
A: The data used should be based on consumer research, surveys, or market analysis. This ensures the map accurately reflects real-world perceptions and preferences.
Q: How many attributes should I include on my map?
A: The number of attributes will depend on the complexity of the market and the specific insights you are seeking. However, it is generally recommended to keep the number of attributes to a minimum (2-4) to avoid overwhelming the map.
Q: How do I determine the best positioning for my brand?
A: The best positioning for your brand will depend on your target audience, your unique value proposition, and the competitive landscape. Analyze the map to identify gaps in the market, areas where competitors are lacking, and potential opportunities for differentiation.
Q: How often should I update my positioning map?
A: It is recommended to update your positioning map regularly, at least once a year, to reflect changes in consumer perceptions, competitor offerings, and market trends.
Tips for Effective Positioning Map Creation
- Focus on Key Attributes: Select attributes that are relevant to consumer choices and accurately reflect the competitive landscape.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure the axes and labels are easily understood and interpreted by consumers.
- Visualize the Data: Use clear and visually appealing graphics to effectively communicate the insights derived from the map.
- Incorporate Feedback: Gather feedback from stakeholders, including marketing, sales, and product development teams, to ensure the map reflects the overall business strategy.
- Continuously Monitor and Update: Regularly review and update the map to reflect changes in the market and consumer preferences.
Conclusion: Navigating the Competitive Landscape with Confidence
Positioning maps are powerful tools that can provide valuable insights into the competitive landscape, consumer perceptions, and opportunities for differentiation. By understanding how consumers perceive your brand and its competitors, you can develop effective marketing strategies, refine your product offerings, and position your brand for success. By embracing the benefits of positioning maps and implementing the best practices outlined in this guide, businesses can navigate the competitive landscape with confidence and achieve sustainable growth.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Positioning Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!