Navigating The Great White North: Understanding Latitude And Longitude In Canadian Geography
Navigating the Great White North: Understanding Latitude and Longitude in Canadian Geography
Related Articles: Navigating the Great White North: Understanding Latitude and Longitude in Canadian Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Great White North: Understanding Latitude and Longitude in Canadian Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Great White North: Understanding Latitude and Longitude in Canadian Geography
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Great White North: Understanding Latitude and Longitude in Canadian Geography
- 3.1 Latitude: Measuring North and South
- 3.2 Longitude: Measuring East and West
- 3.3 Applications of Latitude and Longitude in Canada
- 3.4 FAQs about Latitude and Longitude in Canada
- 3.5 Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude in Canada
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Great White North: Understanding Latitude and Longitude in Canadian Geography
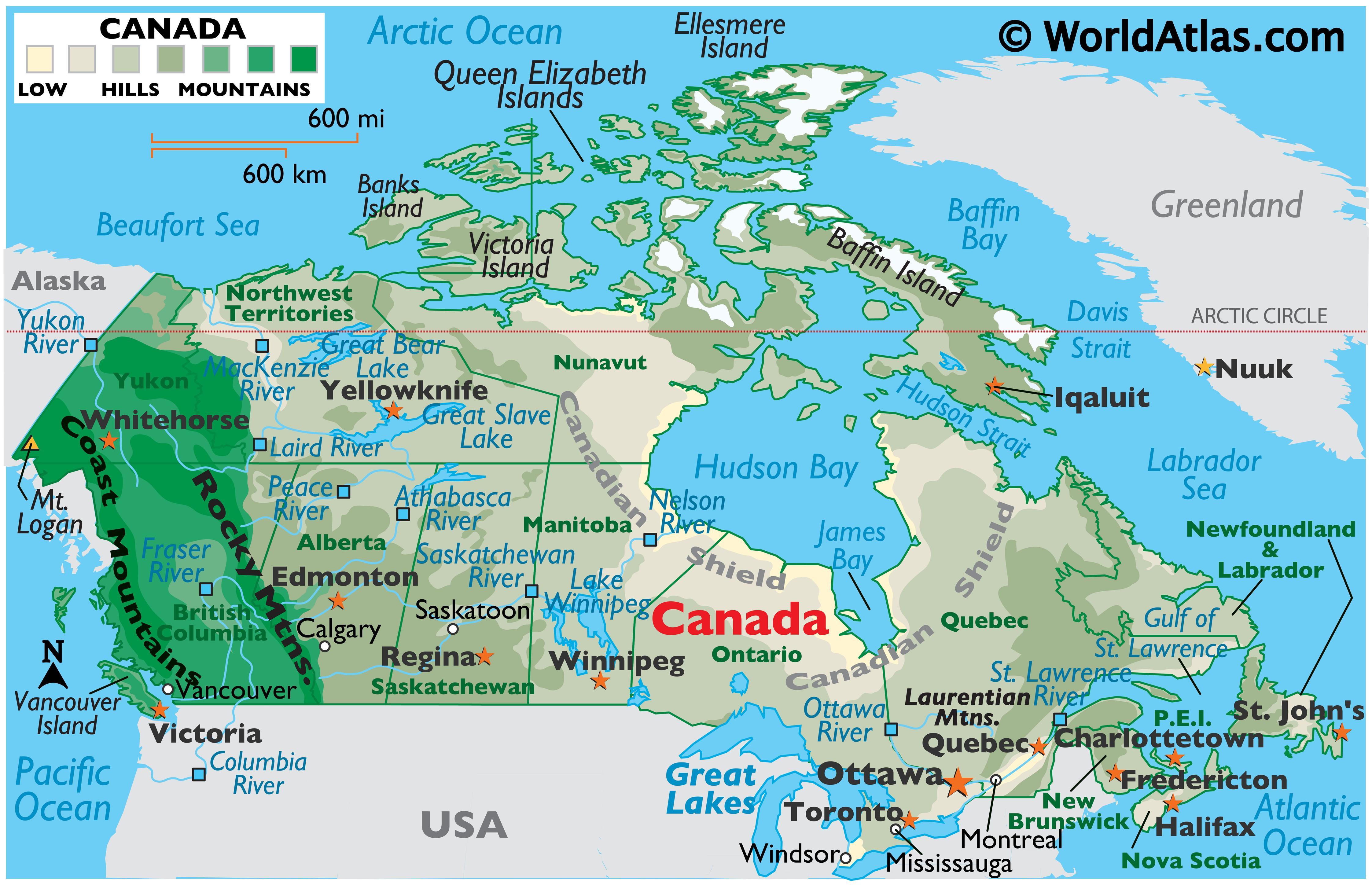
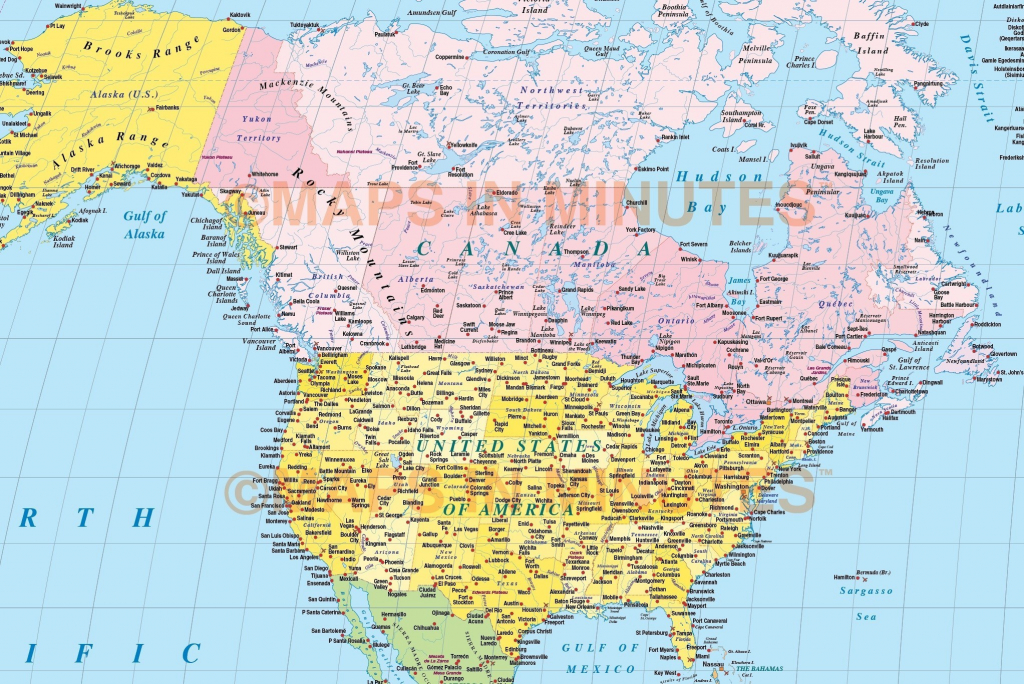
Canada, a vast and diverse country, stretches from the Arctic Ocean to the Great Lakes, encompassing a tapestry of landscapes from towering mountains to expansive prairies. Understanding its geography is crucial for navigating its vast expanse, appreciating its unique features, and appreciating the complexities of its natural and human systems. One of the most fundamental tools for understanding geography is the coordinate system, specifically latitude and longitude. This article delves into the concept of latitude and longitude as applied to Canada, outlining their significance and applications in various fields.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
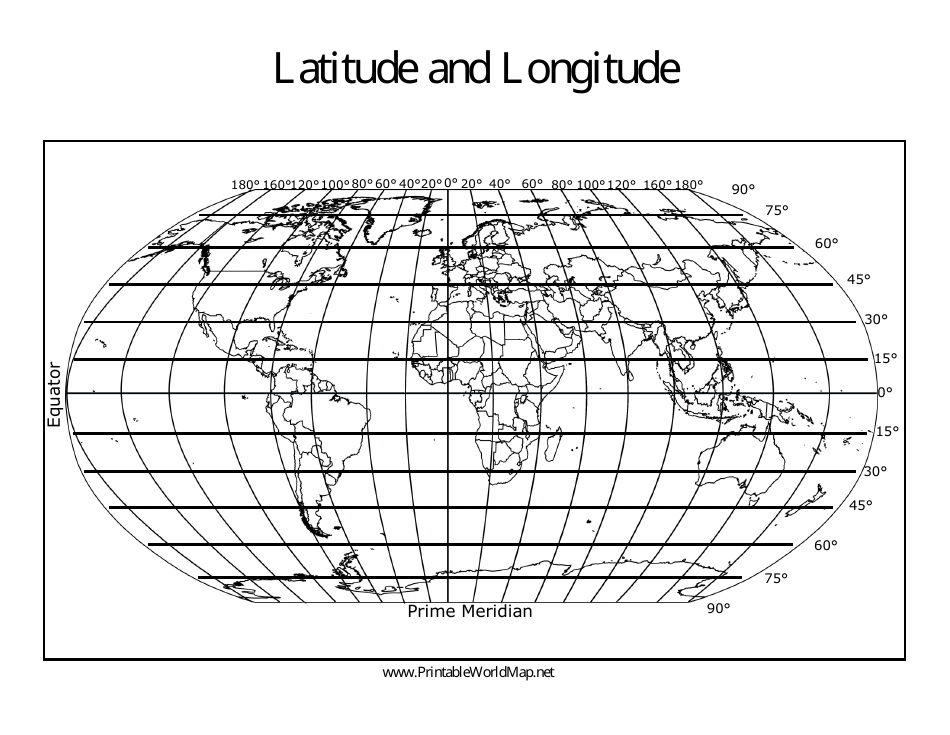
Latitude, often described as the "angular distance" north or south of the equator, is a key component of the geographic coordinate system. The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at zero degrees latitude, serves as the baseline for measuring latitude. Lines of latitude, also known as parallels, run parallel to the equator and are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Northern Hemisphere: Locations north of the equator have positive latitude values, ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the North Pole.
- Southern Hemisphere: Locations south of the equator have negative latitude values, ranging from 0° at the equator to -90° at the South Pole.
Canada, located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere, boasts a wide range of latitudes. Its southernmost point, at the 49th parallel, shares a border with the United States, while its northernmost point, at the 83rd parallel, lies within the Arctic Circle. This vast latitudinal range contributes to Canada’s diverse climate, with warmer temperatures in the south and increasingly colder temperatures further north.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude, the second component of the geographic coordinate system, measures the angular distance east or west of the prime meridian. The prime meridian, an imaginary line passing through Greenwich, England, serves as the zero-degree reference point for measuring longitude. Lines of longitude, also known as meridians, converge at the North and South Poles and are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
- Eastern Hemisphere: Locations east of the prime meridian have positive longitude values, ranging from 0° at the prime meridian to 180°.
- Western Hemisphere: Locations west of the prime meridian have negative longitude values, ranging from 0° at the prime meridian to -180°.
Canada, spanning the western half of the North American continent, encompasses a wide range of longitudes. Its easternmost point, at approximately -60° longitude, lies in Newfoundland and Labrador, while its westernmost point, at approximately -130° longitude, lies in British Columbia. This vast longitudinal range contributes to Canada’s diverse time zones, with the country spanning six time zones from Atlantic Standard Time in the east to Pacific Standard Time in the west.
Applications of Latitude and Longitude in Canada
The use of latitude and longitude extends far beyond simply understanding Canada’s geographical boundaries. This coordinate system plays a critical role in various fields, including:
- Navigation and Mapping: Latitude and longitude form the foundation of modern navigation systems, including GPS (Global Positioning System) and mapping applications. They allow for precise location determination and are essential for navigating across Canada’s vast and diverse landscapes.
- Climate and Weather Forecasting: Latitude plays a crucial role in determining climate patterns across Canada. The country’s northern latitudes experience long, cold winters and short, cool summers, while its southern latitudes have milder winters and warmer summers. Understanding latitude helps forecasters predict weather patterns and provide accurate weather information.
- Resource Management: Latitude and longitude are essential for managing Canada’s natural resources, including forestry, mining, and fishing. Precise location data allows for efficient resource extraction, environmental monitoring, and conservation efforts.
- Emergency Response: Latitude and longitude are vital for emergency response teams, enabling them to quickly locate incidents and dispatch appropriate resources. This is particularly important in remote areas where traditional landmarks may be limited.
- Research and Data Analysis: Latitude and longitude are essential for collecting and analyzing data across various fields, including environmental science, social studies, and economics. By associating data with specific locations, researchers can gain valuable insights into spatial patterns and trends.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude in Canada
1. What are the latitude and longitude coordinates of Canada’s capital city, Ottawa?
- Ottawa’s coordinates are approximately 45.4215° N, -75.6972° W.
2. How does latitude affect the length of daylight hours in Canada?
- Locations at higher latitudes experience longer periods of daylight during the summer months and shorter periods of daylight during the winter months due to the Earth’s tilt. This phenomenon, known as the "midnight sun" in the far north, results in extended periods of daylight during the summer solstice.
3. How does longitude affect time zones in Canada?
- As the Earth rotates, different locations experience sunrise and sunset at different times. Longitude is used to define time zones, with each time zone spanning approximately 15 degrees of longitude. Canada, spanning six time zones, experiences a wide range of time differences across its vast territory.
4. Are there any specific locations in Canada with significant latitude or longitude coordinates?
- Yes, several locations in Canada hold significance due to their unique latitude or longitude coordinates. For example, the 49th parallel, marking the border between Canada and the United States, is a prominent geographical feature. Similarly, the 100th meridian, running through the Prairie provinces, serves as a historical and geographical reference point.
5. How can I find the latitude and longitude coordinates of a specific location in Canada?
- Numerous online tools and applications allow you to find the latitude and longitude coordinates of any location. Popular options include Google Maps, Bing Maps, and GPS devices.
Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude in Canada
- Familiarize yourself with the coordinate system: Understanding the concepts of latitude and longitude is essential for interpreting maps and navigating across Canada.
- Utilize online tools and applications: Numerous online tools and applications can help you find latitude and longitude coordinates, convert between different coordinate formats, and visualize locations on maps.
- Consider the impact of latitude and longitude on various aspects of Canadian geography: Latitude influences climate, daylight hours, and plant and animal life, while longitude affects time zones and cultural differences.
- Use latitude and longitude to plan your travels: Knowing the coordinates of your destination can help you navigate efficiently and discover hidden gems across Canada’s vast landscape.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude, fundamental tools for understanding geography, provide a framework for navigating, analyzing, and appreciating the vast and diverse landscape of Canada. From understanding climate patterns to managing resources and navigating across its vast expanse, this coordinate system plays a critical role in various aspects of Canadian life. By understanding the concepts of latitude and longitude, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and nuances of Canada’s geography and unlock a world of possibilities for exploring its unique features.
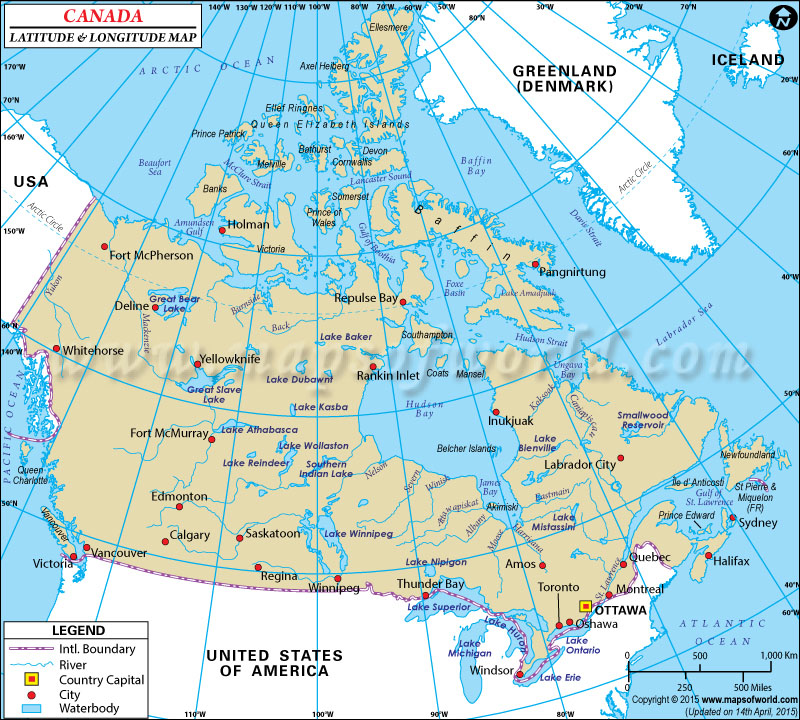


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Great White North: Understanding Latitude and Longitude in Canadian Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!