Navigating the Gulf of Mexico: Understanding its Dynamic Weather Patterns
Related Articles: Navigating the Gulf of Mexico: Understanding its Dynamic Weather Patterns
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Gulf of Mexico: Understanding its Dynamic Weather Patterns. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Gulf of Mexico: Understanding its Dynamic Weather Patterns
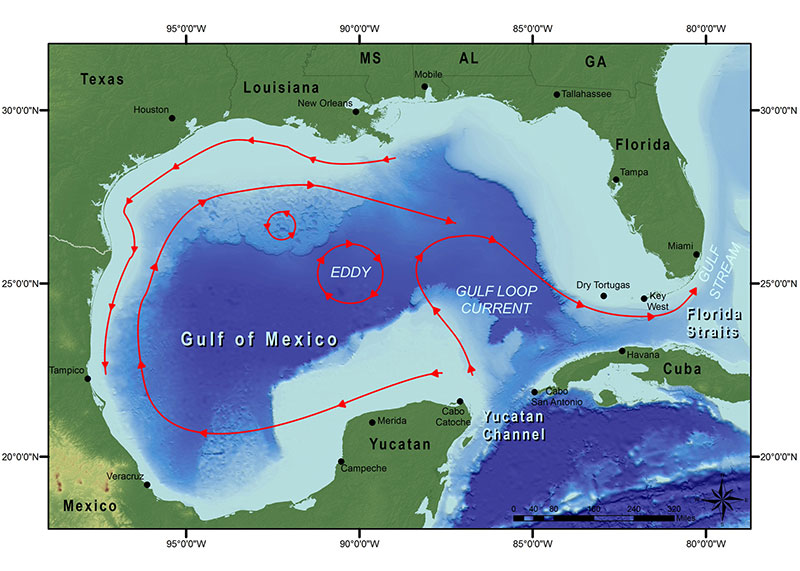
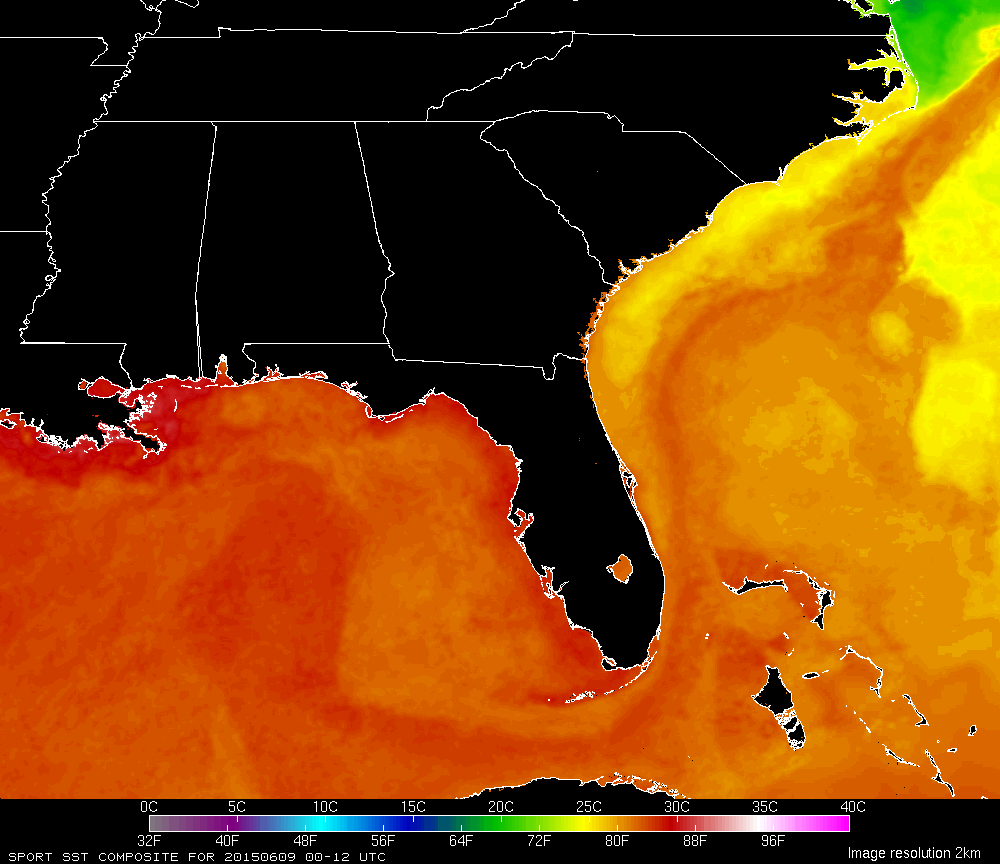
The Gulf of Mexico, a vast body of water cradled by the southeastern United States, Mexico, and Cuba, is a dynamic and complex ecosystem. Its weather patterns are intricately woven with the broader climate of the region, impacting everything from daily life to major industries. Understanding the intricacies of the Gulf of Mexico’s weather is crucial for navigating its waters, preparing for potential storms, and appreciating the delicate balance of its ecosystem.
A Deep Dive into the Gulf’s Weather Dynamics
The Gulf of Mexico’s weather is shaped by a confluence of factors, including:
- Latitude: Situated between 18° and 30° North, the Gulf lies within the tropical and subtropical zones, experiencing warm temperatures and high humidity year-round.
- Ocean Currents: The Gulf Stream, a powerful warm current, flows northward along the eastern coast of the United States, influencing the Gulf’s temperature and bringing warm, moist air to the region.
- Trade Winds: Steady winds blowing from east to west, driven by the Earth’s rotation, influence the Gulf’s surface currents and contribute to the formation of tropical storms.
- Topographical Features: The surrounding landmasses, including the Appalachian Mountains and the Mexican Plateau, play a role in directing air flow and influencing precipitation patterns.
- Atmospheric Pressure: The Gulf is a breeding ground for low-pressure systems, which can develop into tropical storms and hurricanes.
Seasonal Variations: From Gentle Breezes to Powerful Hurricanes
The Gulf of Mexico’s weather exhibits distinct seasonal variations:
- Spring (March-May): The transition from winter to summer brings increasing sunshine and warmer temperatures. The Gulf is still relatively calm, with occasional thunderstorms.
- Summer (June-August): The warmest period, characterized by high humidity, intense sunshine, and frequent thunderstorms. This is also the peak season for tropical storms and hurricanes.
- Fall (September-November): Temperatures begin to cool, but the Gulf remains a hurricane threat. The Atlantic hurricane season officially ends on November 30th.
- Winter (December-February): Cooler temperatures and occasional cold fronts bring sporadic rain and wind. The Gulf’s waters are still relatively warm, making it a popular destination for winter fishing and boating.
The Impact of the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, a powerful ocean current, significantly influences the Gulf’s weather. It transports warm, tropical waters northward, moderating the climate of the southeastern United States. The Gulf Stream’s influence extends beyond the Gulf, reaching as far as northwestern Europe, where it helps to keep the climate milder than it would otherwise be.
The Threat of Hurricanes
The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most hurricane-prone regions in the world. The warm waters and low wind shear provide ideal conditions for the development of tropical storms and hurricanes. These storms can cause significant damage to coastal areas, leading to flooding, power outages, and loss of life.
Understanding the Gulf’s Weather: Benefits and Importance
Understanding the Gulf of Mexico’s weather patterns is essential for:
- Safe Navigation: Mariners rely on accurate weather forecasts to navigate the Gulf safely, avoiding dangerous storms and navigating strong currents.
- Coastal Development: Coastal communities need to plan for the potential impacts of hurricanes and other severe weather events, including storm surge and flooding.
- Fisheries and Marine Life: The Gulf’s weather patterns influence the distribution and abundance of marine life, impacting fishing industries and the health of the ecosystem.
- Tourism and Recreation: Tourists and recreational boaters need to be aware of weather conditions to ensure safe and enjoyable experiences.
- Climate Research: The Gulf of Mexico is a crucial area for studying climate change, as its weather patterns are sensitive to changes in global temperatures and ocean currents.
FAQs about the Gulf of Mexico’s Weather
1. What are the most common weather hazards in the Gulf of Mexico?
The most common weather hazards in the Gulf of Mexico are:
- Tropical Storms and Hurricanes: The Gulf is a major hurricane breeding ground, with the peak season occurring from June to November.
- Thunderstorms: Frequent thunderstorms can bring heavy rain, lightning, and strong winds.
- Fog: Fog can reduce visibility, making navigation hazardous.
- Strong Winds: Strong winds can create rough seas, making boating dangerous.
- Cold Fronts: Cold fronts can bring strong winds, heavy rain, and occasionally hail.
2. What are the best times to visit the Gulf of Mexico for good weather?
The best times to visit the Gulf of Mexico for good weather are:
- Spring (March-May): Pleasant temperatures, sunshine, and calm seas.
- Fall (September-November): Warm temperatures, but with the possibility of hurricanes.
3. How do I stay safe during hurricane season in the Gulf of Mexico?
Here are some tips for staying safe during hurricane season:
- Stay informed: Monitor weather forecasts and warnings from reliable sources, such as the National Hurricane Center.
- Have a plan: Develop an evacuation plan and know where to go if a hurricane threatens your area.
- Secure your property: Secure loose objects, trim trees, and board up windows.
- Prepare a hurricane kit: Stock up on essential supplies, such as food, water, batteries, and first-aid supplies.
4. How does climate change affect the Gulf of Mexico’s weather?
Climate change is expected to intensify the Gulf of Mexico’s weather patterns, leading to:
- More frequent and intense hurricanes: Warmer ocean waters provide more energy for hurricanes to develop and intensify.
- Sea level rise: Rising sea levels increase the risk of storm surge flooding.
- Increased rainfall: Warmer temperatures lead to more evaporation and precipitation.
Conclusion
The Gulf of Mexico’s weather is a complex and ever-changing phenomenon, influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding these patterns is crucial for navigating its waters safely, mitigating the risks of severe weather events, and appreciating the delicate balance of its ecosystem. As climate change continues to impact the world’s oceans, understanding and adapting to the changing weather patterns of the Gulf of Mexico will become increasingly important for the region’s future.

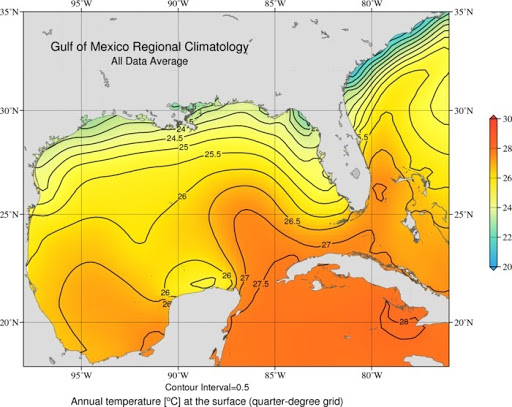


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Gulf of Mexico: Understanding its Dynamic Weather Patterns. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!