Navigating the Waters: Understanding Shellfish Safety Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding Shellfish Safety Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters: Understanding Shellfish Safety Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waters: Understanding Shellfish Safety Maps
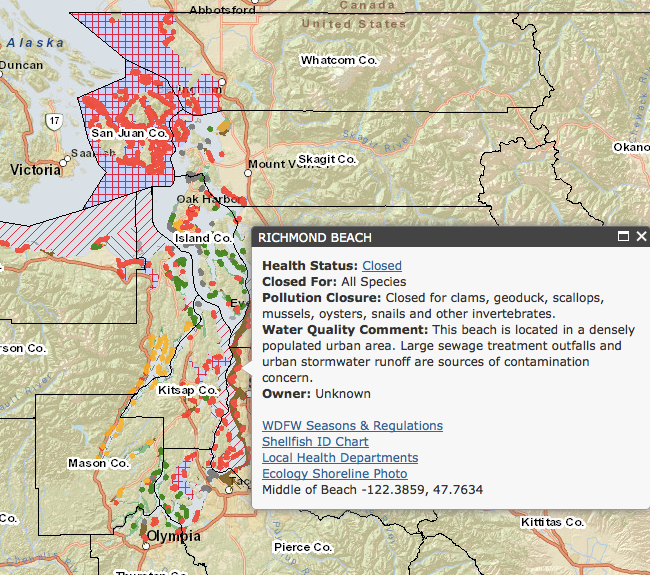
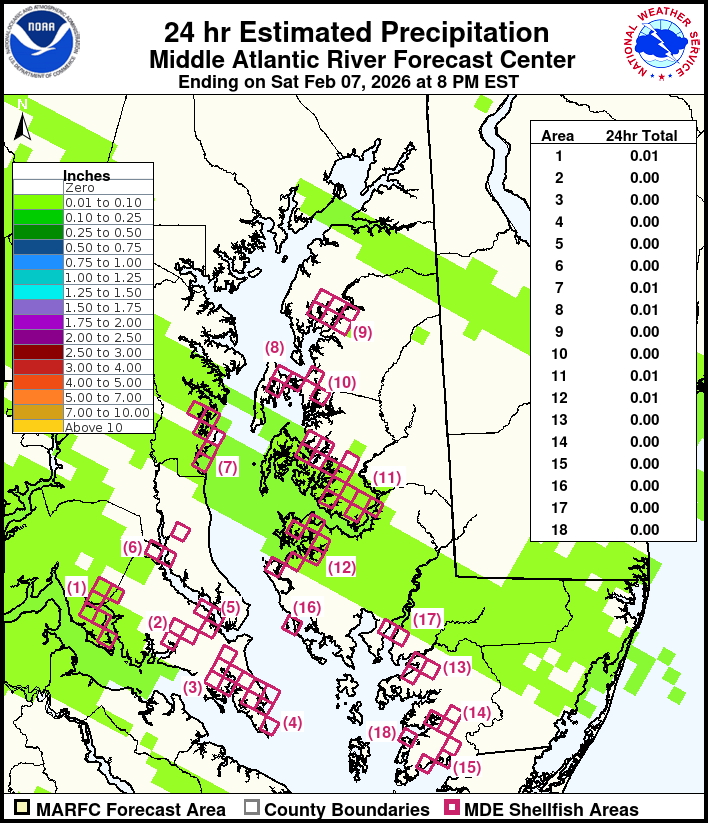
Shellfish, a culinary delight enjoyed worldwide, are also susceptible to contamination, posing potential health risks to consumers. To mitigate these risks and safeguard public health, authorities implement stringent monitoring programs and issue shellfish safety maps. These maps serve as crucial tools for both consumers and industry professionals, providing vital information about the safety of shellfish harvested from specific areas.
The Importance of Shellfish Safety Maps
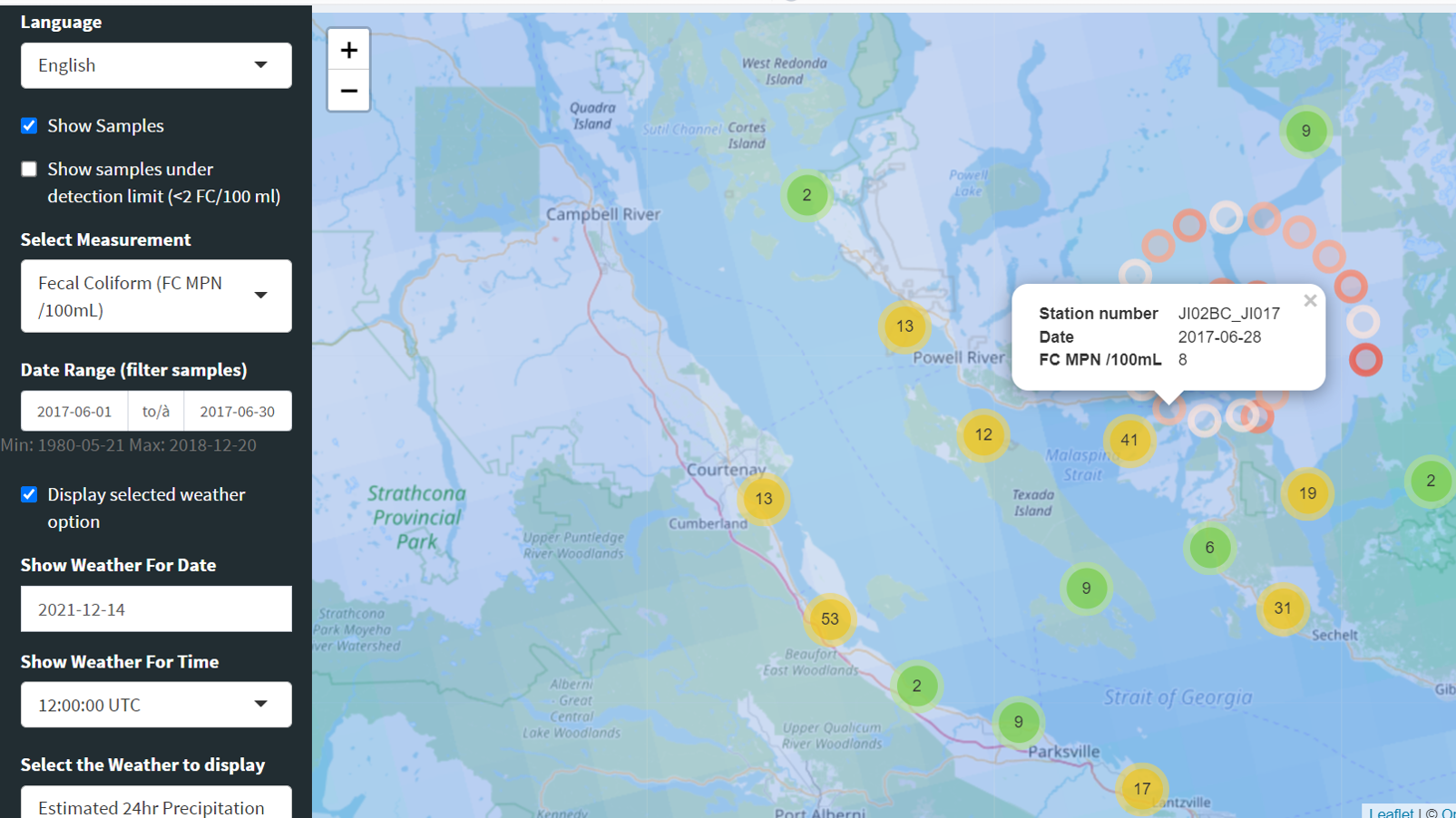
Shellfish, particularly bivalve mollusks like oysters, mussels, clams, and scallops, are filter feeders. This means they draw in surrounding water, filtering out plankton and other microscopic organisms, including harmful bacteria, viruses, and toxins. These contaminants can accumulate in shellfish tissue, making them unsafe for consumption if harvested from contaminated areas.
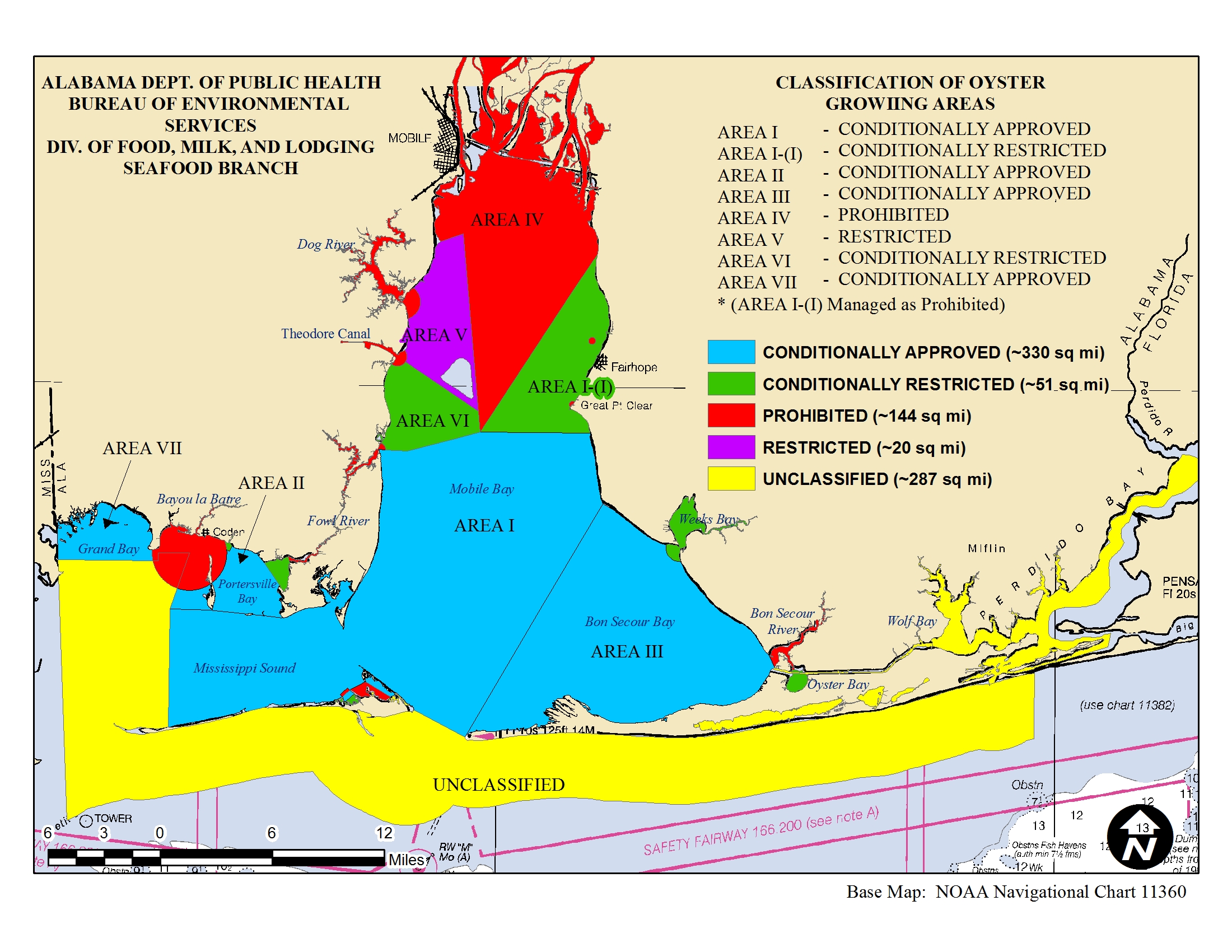
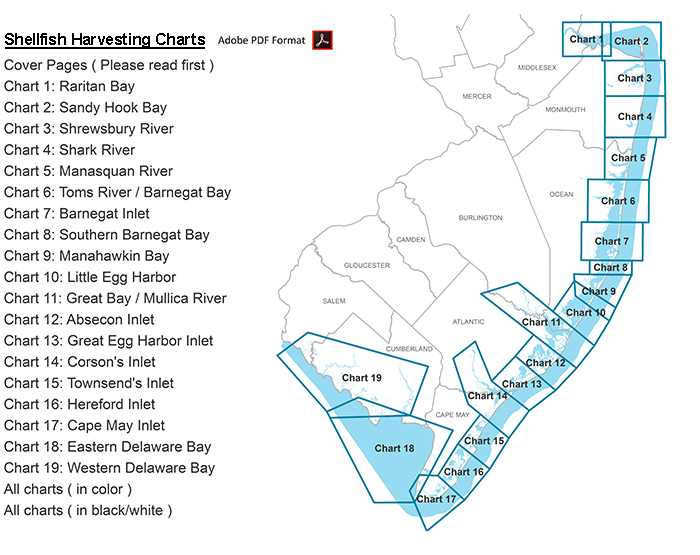
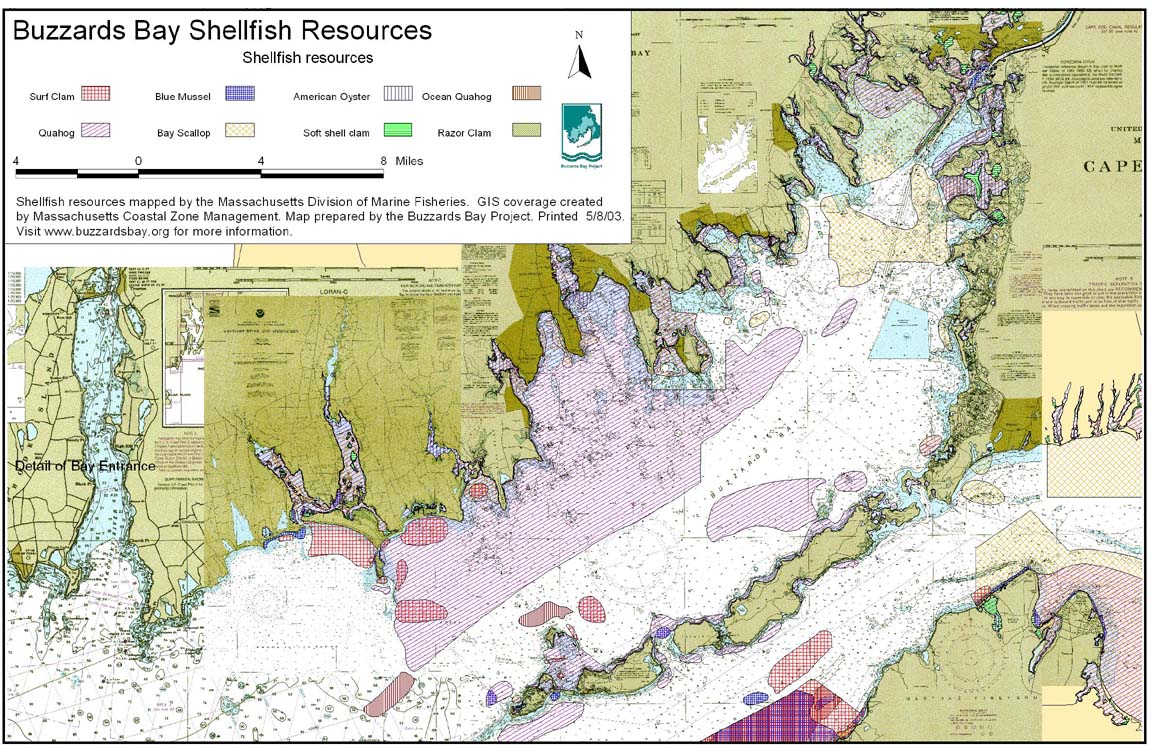
Shellfish safety maps, also known as shellfish harvesting areas maps, are created by government agencies responsible for regulating shellfish safety. They depict geographic zones where shellfish harvesting is permitted or restricted, based on the presence of contaminants. These maps are regularly updated to reflect the latest water quality data and environmental conditions.
Understanding the Zones
Shellfish safety maps typically depict areas categorized into different zones, each with specific restrictions:
- Open Areas: These zones are deemed safe for shellfish harvesting and consumption. They meet all regulatory standards for water quality and contaminant levels.
- Conditional Areas: These zones may have elevated levels of certain contaminants, but they are still considered safe for harvesting under specific conditions. This might involve limitations on harvesting times, species, or size limits.
- Closed Areas: These zones are deemed unsafe for shellfish harvesting due to high levels of contaminants. Harvesting and consumption of shellfish from these areas are prohibited.
Factors Influencing Shellfish Safety
Several factors contribute to the contamination of shellfish harvesting areas, including:
- Sewage Discharge: Untreated or poorly treated sewage can introduce harmful bacteria and viruses into waterways.
- Agricultural Runoff: Runoff from agricultural fields can carry fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste, contaminating water sources.
- Industrial Discharge: Industrial wastewater can contain heavy metals, chemicals, and other toxins that can accumulate in shellfish.
- Harmful Algal Blooms: Certain types of algae produce toxins that can be harmful to humans and accumulate in shellfish.
- Natural Occurrences: Natural events like heavy rainfall, storms, and flooding can cause water quality degradation and increase the risk of contamination.
How Shellfish Safety Maps are Used
Shellfish safety maps serve a crucial role in protecting public health by:
- Guiding Shellfish Harvesters: They provide clear information about permitted and restricted areas, ensuring that only safe shellfish are harvested.
- Informing Consumers: They allow consumers to make informed decisions about the safety of shellfish they purchase or consume.
- Facilitating Enforcement: They provide a framework for regulatory agencies to enforce harvesting restrictions and monitor compliance.
- Supporting Research: They contribute to scientific research by providing data on the distribution and levels of contaminants in shellfish harvesting areas.
Benefits of Shellfish Safety Maps
The implementation of shellfish safety maps offers significant benefits:
- Reduced Risk of Foodborne Illness: By restricting harvesting in contaminated areas, maps help prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses caused by contaminated shellfish.
- Protection of Public Health: They safeguard consumers from the potential health risks associated with consuming contaminated shellfish.
- Economic Sustainability: By ensuring the safety of shellfish harvests, they support the economic viability of the shellfish industry.
- Environmental Protection: They contribute to the overall health and sustainability of aquatic ecosystems by promoting responsible harvesting practices.
Frequently Asked Questions about Shellfish Safety Maps
Q: Where can I find a shellfish safety map for my area?
A: Shellfish safety maps are typically published by state or regional government agencies responsible for regulating shellfish safety. These maps can often be found on their websites or obtained through local seafood retailers or shellfish harvesters.
Q: How often are shellfish safety maps updated?
A: Shellfish safety maps are regularly updated based on the latest water quality data and environmental conditions. The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific area and the level of risk.
Q: What should I do if I find shellfish harvested from a closed area?
A: If you find shellfish harvested from a closed area, it is important to report this to the relevant authorities. Do not consume the shellfish as they may be contaminated and pose a health risk.
Q: Are there any other resources available for understanding shellfish safety?
A: In addition to shellfish safety maps, other resources can provide information about shellfish safety, including:
- State or regional shellfish safety websites
- Seafood safety brochures or pamphlets
- Local seafood retailers or shellfish harvesters
- National seafood safety organizations
Tips for Ensuring Shellfish Safety
- Purchase Shellfish from Reputable Sources: Always purchase shellfish from reputable retailers who obtain their products from approved harvesting areas.
- Check Shellfish Safety Maps: Before consuming shellfish, consult the shellfish safety map for your area to ensure the shellfish you are purchasing or harvesting are safe.
- Inspect Shellfish for Quality: Ensure that the shellfish you purchase are fresh, have closed shells, and are free of any signs of spoilage.
- Cook Shellfish Thoroughly: Cook shellfish thoroughly to kill any harmful bacteria or viruses that may be present.
- Store Shellfish Properly: Store shellfish in the refrigerator at a temperature of 40°F or below. Do not store shellfish at room temperature.
Conclusion
Shellfish safety maps are essential tools for protecting public health and ensuring the safety of shellfish harvested from specific areas. By understanding the zones, factors influencing shellfish safety, and the benefits of these maps, consumers, industry professionals, and regulatory agencies can work together to promote safe and sustainable shellfish harvesting practices.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters: Understanding Shellfish Safety Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!