The Ethnic Mosaic of Syria: A Complex Tapestry of Identities
Related Articles: The Ethnic Mosaic of Syria: A Complex Tapestry of Identities
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Ethnic Mosaic of Syria: A Complex Tapestry of Identities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ethnic Mosaic of Syria: A Complex Tapestry of Identities

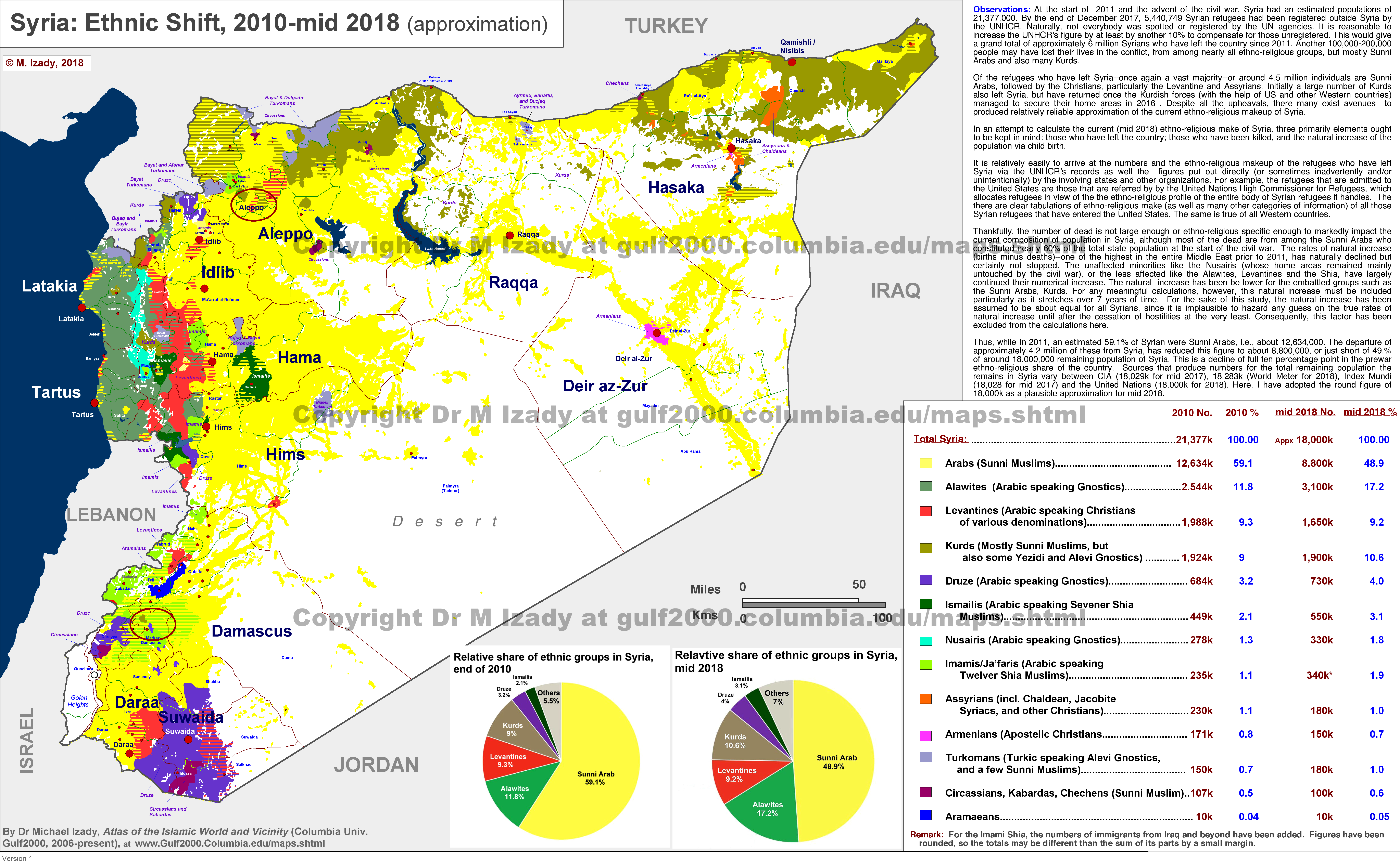
Syria, a nation nestled at the crossroads of civilizations, boasts a rich and intricate ethnic tapestry woven from diverse threads. This intricate mosaic of identities has shaped the country’s history, culture, and social fabric, contributing to both its vibrant dynamism and its enduring challenges. Understanding the ethnic map of Syria is crucial for comprehending the nation’s past, present, and potential future.
A Diverse Landscape of Ethnicity:
Syria’s ethnic makeup is characterized by a confluence of Arab, Kurdish, Turkmen, Armenian, Circassian, and other smaller groups. While Arabs constitute the largest ethnic group, representing approximately 90% of the population, the remaining 10% represent a spectrum of minorities, each with its unique history, language, and cultural traditions.
The Arab Majority:
The Arab population of Syria, primarily Sunni Muslim, is further subdivided into various tribal groups, each with its own distinct customs and affiliations. These tribes, often geographically concentrated, have played a significant role in shaping Syria’s political landscape and social dynamics.
The Kurdish Minority:
The Kurds, a significant minority group primarily concentrated in the northeastern regions, have long sought autonomy and cultural recognition. Their struggle for self-determination has been a recurring theme in Syrian history, marked by periods of conflict and negotiation.
Turkmen and Circassian Communities:
The Turkmen, predominantly Sunni Muslim, are scattered throughout Syria, particularly in the north and east. They have historically maintained a strong sense of cultural identity, preserving their language and traditions. The Circassians, another significant minority, are predominantly Sunni Muslim and primarily reside in the northwestern regions. They arrived in Syria following the Russian conquest of the Caucasus in the 19th century.
Armenian and Other Minorities:
Armenians, mostly Christian, have a long history in Syria, dating back to ancient times. Their presence is particularly prominent in Aleppo and Damascus, where they have contributed significantly to the nation’s economic and cultural life. Other smaller minorities, including Assyrians, Chaldeans, and Arameans, also enrich the Syrian ethnic landscape, each with its distinct religious and cultural heritage.
The Impact of Ethnic Diversity:
Syria’s ethnic diversity has had both positive and negative impacts on its development. On the one hand, it has fostered a rich cultural exchange, contributing to a vibrant artistic and intellectual landscape. The country has long been a hub for trade and cultural interaction, with its diverse ethnic groups playing a vital role in shaping this dynamic exchange.
On the other hand, ethnic differences have also been a source of tension and conflict. Historical grievances, competing claims to resources, and political maneuvering have often exacerbated ethnic divisions, leading to periods of unrest and violence.
The Syrian Civil War and its Ethnic Dimensions:
The Syrian Civil War, which erupted in 2011, has further complicated the ethnic landscape, exacerbating existing tensions and creating new divides. While the conflict initially arose from a desire for political reform, it quickly evolved into a complex and multifaceted struggle, with ethnic and sectarian dimensions playing a significant role.
Various armed groups, including those with explicitly ethnic or sectarian agendas, have emerged, adding another layer of complexity to the conflict. This has led to a fragmentation of Syrian society, with different ethnic and religious groups often aligning with opposing sides in the war.
The Future of Syria’s Ethnic Landscape:
The future of Syria’s ethnic landscape remains uncertain. The outcome of the civil war will undoubtedly have a profound impact on the country’s ethnic composition and the relationships between its various groups.
Reconciliation and rebuilding will require addressing the underlying causes of ethnic tensions and fostering a sense of shared identity and belonging. This will be a complex and challenging task, requiring a commitment to dialogue, inclusion, and respect for diversity.
FAQs on the Ethnic Map of Syria:
Q: What is the largest ethnic group in Syria?
A: Arabs constitute the largest ethnic group in Syria, representing approximately 90% of the population.
Q: Where are the Kurds primarily concentrated in Syria?
A: The Kurdish population is primarily concentrated in the northeastern regions of Syria.
Q: What is the significance of the Turkmen and Circassian communities in Syria?
A: Both the Turkmen and Circassians have historically maintained a strong sense of cultural identity, preserving their language and traditions.
Q: What role have ethnic minorities played in Syrian history and culture?
A: Ethnic minorities have contributed significantly to Syria’s cultural and economic development, enriching the nation’s artistic, intellectual, and commercial life.
Q: How has the Syrian Civil War affected the ethnic landscape?
A: The civil war has exacerbated existing ethnic tensions, created new divides, and led to a fragmentation of Syrian society.
Q: What are the challenges facing Syria in terms of its ethnic diversity?
A: Syria faces challenges in addressing historical grievances, managing competing claims to resources, and promoting inter-ethnic dialogue and reconciliation.
Tips for Understanding Syria’s Ethnic Landscape:
- Engage with diverse sources: Seek out information from a variety of perspectives, including Syrian scholars, journalists, and community leaders.
- Explore the historical context: Understanding the historical roots of ethnic relations in Syria can provide valuable insights.
- Recognize the complexities: The ethnic landscape of Syria is complex and nuanced, with overlapping identities and evolving relationships.
- Emphasize empathy and understanding: Approach the subject with sensitivity, acknowledging the diverse experiences and perspectives of different ethnic groups.
Conclusion:
The ethnic map of Syria is a testament to the country’s rich history and cultural diversity. While ethnic differences have contributed to both its dynamism and its challenges, understanding and respecting this complex tapestry is crucial for fostering a more inclusive and peaceful future. The path towards reconciliation and rebuilding will require a commitment to dialogue, inclusion, and a recognition of the shared humanity that binds all Syrians together.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ethnic Mosaic of Syria: A Complex Tapestry of Identities. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!