Uncovering Belarus: A Landlocked Jewel in Eastern Europe
Related Articles: Uncovering Belarus: A Landlocked Jewel in Eastern Europe
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Uncovering Belarus: A Landlocked Jewel in Eastern Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering Belarus: A Landlocked Jewel in Eastern Europe
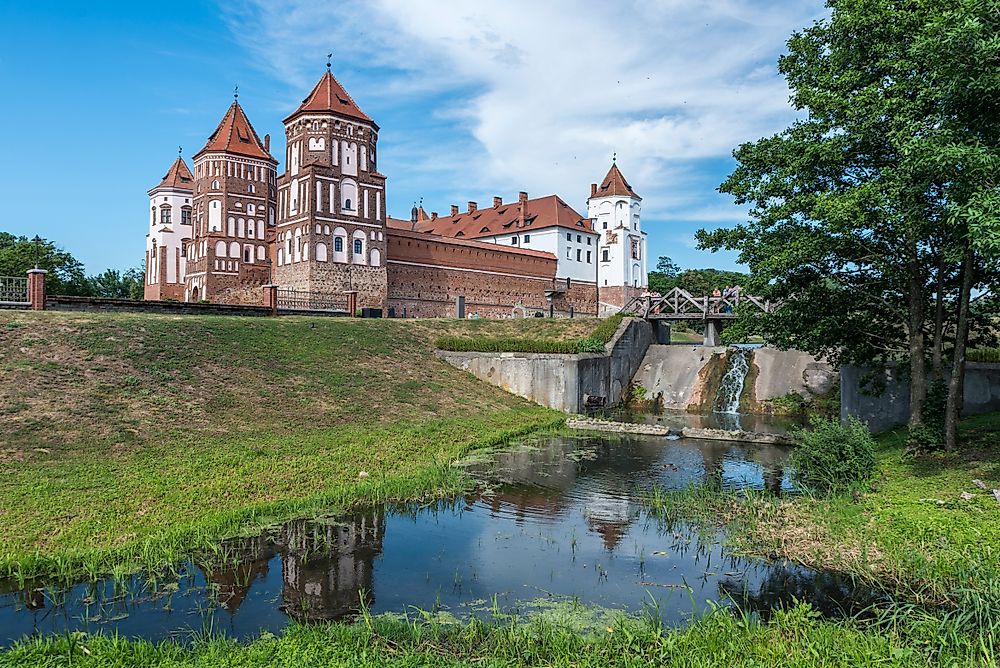

Belarus, a nation often referred to as the "last dictatorship in Europe," occupies a unique position in the Eastern European landscape. Its strategic location, nestled between Russia, Ukraine, Poland, and Lithuania, has played a significant role in shaping its history, culture, and contemporary geopolitical significance. This article delves into the geographic context of Belarus, exploring its borders, neighboring countries, and the physical features that contribute to its distinct character.
A Landlocked Haven:
Belarus, a landlocked country, lacks access to any sea or ocean. This geographical feature has influenced its economic development and foreign policy, pushing it towards stronger ties with its neighboring landlocked nations, particularly Russia. However, this lack of access to maritime trade routes has also presented challenges, limiting its potential for global trade and economic diversification.
Navigating the Borders:
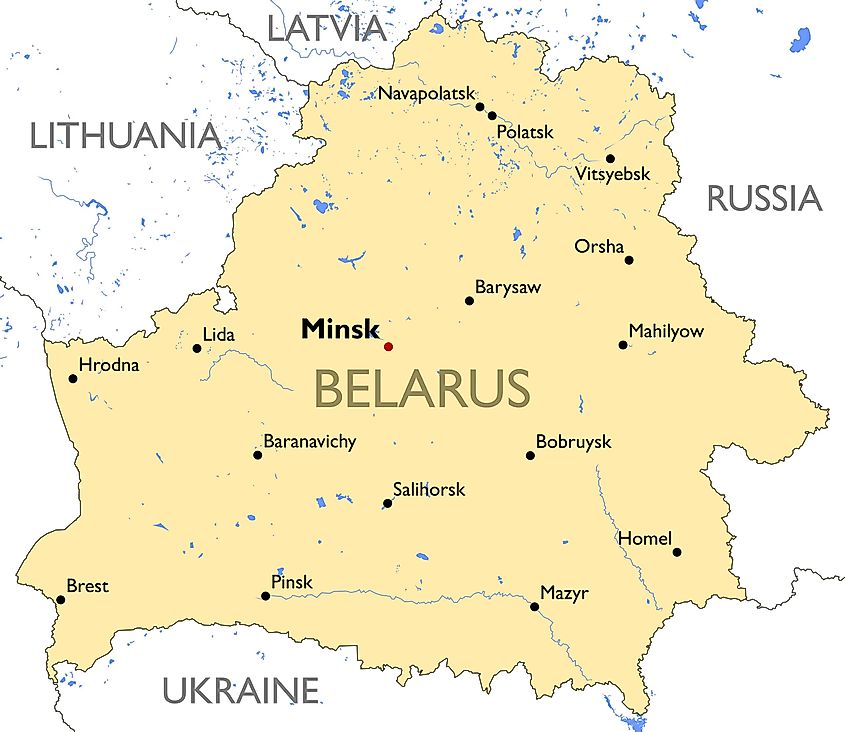
Belarus shares borders with five countries, each contributing to its complex geopolitical landscape:
- Russia: The longest and most influential border, spanning over 1,000 kilometers, reflects a historical and cultural connection that runs deep. The two countries have a close political and economic partnership, with Russia playing a crucial role in Belarus’s energy security and economic stability.
- Ukraine: The border with Ukraine, stretching over 1,000 kilometers, has become a focal point of regional tensions in recent years. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has significantly impacted Belarus, both politically and economically.
- Poland: The border with Poland, spanning over 400 kilometers, represents a historical connection, marked by periods of both cooperation and conflict. The two countries have been working to improve relations in recent years, particularly in the economic sphere.
- Lithuania: The border with Lithuania, stretching over 160 kilometers, is characterized by a complex history, marked by periods of both cooperation and tension. The two countries have worked to develop economic ties and address shared concerns regarding regional security.
- Latvia: The shortest border, spanning over 140 kilometers, reflects a historical connection with Latvia, marked by periods of both cooperation and conflict. The two countries have been working to improve relations in recent years, particularly in the economic sphere.
Land of Forests and Rivers:
The Belarusian landscape is characterized by its rolling plains, vast forests, and numerous rivers. The country is known as the "Land of Forests," with approximately 40% of its territory covered by forests. These forests are home to a rich biodiversity, including wolves, bears, lynx, and a variety of bird species.
The country is also crisscrossed by a network of rivers, including the Dnieper, the Western Dvina, and the Neman. These rivers have played a significant role in the country’s history, providing transportation routes and sources of water. They also contribute to the beauty and ecological richness of the Belarusian landscape.
A Strategic Crossroads:
Belarus’s location at the crossroads of Eastern and Western Europe has made it a strategically important country throughout history. This strategic location has been both a blessing and a curse. While it has allowed Belarus to act as a bridge between East and West, it has also made it vulnerable to external influences and conflicts.
In the contemporary world, Belarus’s strategic location continues to be a factor in its geopolitical significance. Its proximity to Russia, Ukraine, and the European Union makes it a key player in regional security and stability. The country’s close ties with Russia have made it a target of Western sanctions, while its potential to act as a bridge between Russia and the West has been recognized by various actors.
Navigating the Political Landscape:
Belarus has been governed by an authoritarian regime since the collapse of the Soviet Union. Its political system is characterized by a strong presidency, limited political freedom, and restricted media access. The country has faced criticism from international organizations for its human rights record and lack of democratic institutions.
However, Belarus is also a country of resilience and adaptability. Despite its challenges, it has managed to maintain its independence and preserve its cultural identity. It has also made significant strides in economic development, particularly in the IT sector.
The Promise of Potential:
Despite its political and economic challenges, Belarus possesses a number of assets that offer potential for future growth and development. These assets include:
- A skilled workforce: Belarus has a well-educated workforce with a strong tradition of technical expertise. This human capital can be leveraged to attract foreign investment and develop new industries.
- Rich natural resources: The country possesses a variety of natural resources, including potash, timber, and natural gas. These resources can be used to develop a more diversified economy and reduce dependence on Russia.
- A strategic location: Belarus’s location at the crossroads of Eastern and Western Europe can be used to develop a thriving trade and transport hub. The country can act as a bridge between Russia and the West, facilitating economic cooperation and cultural exchange.
- A growing IT sector: Belarus has emerged as a regional leader in the IT sector, with a thriving startup ecosystem and a growing number of tech companies. This sector has the potential to drive economic growth and create new jobs.
FAQs
Q: What is the capital of Belarus?
A: The capital of Belarus is Minsk.
Q: What is the official language of Belarus?
A: The official language of Belarus is Belarusian, although Russian is widely spoken.
Q: What is the currency of Belarus?
A: The currency of Belarus is the Belarusian ruble.
Q: What is the population of Belarus?
A: The population of Belarus is approximately 9.5 million.
Q: What is the climate like in Belarus?
A: Belarus has a humid continental climate with warm summers and cold winters.
Q: What are some of the main industries in Belarus?
A: The main industries in Belarus include agriculture, manufacturing, energy, and IT.
Q: What are some of the major tourist attractions in Belarus?
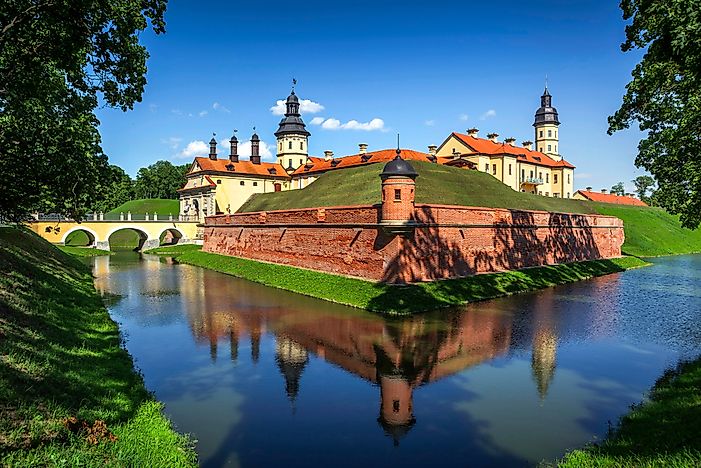
A: Some of the major tourist attractions in Belarus include the Mir Castle, the Nesvizh Castle, and the Brest Fortress.
Tips for Visiting Belarus:
- Learn some basic Russian: While English is not widely spoken, some basic Russian phrases will go a long way in communicating with locals.
- Be respectful of local customs: Belarus is a country with strong traditions and customs. It is important to be respectful of these traditions when visiting.
- Enjoy the natural beauty: Belarus is a country of stunning natural beauty. Take some time to explore the forests, lakes, and rivers.
- Try the local cuisine: Belarusian cuisine is hearty and flavorful. Be sure to try some of the local specialties, such as draniki (potato pancakes) and babka (a sweet bread).
Conclusion:
Belarus, a landlocked nation in Eastern Europe, stands as a testament to the complex interplay of history, geography, and culture. Its strategic location, bordering Russia, Ukraine, Poland, Lithuania, and Latvia, has shaped its political, economic, and social landscape. Despite its challenges, Belarus possesses a unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and economic potential, making it a country worth exploring and understanding.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering Belarus: A Landlocked Jewel in Eastern Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!