Understanding Nevada’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide To The State’s Fault Lines
Understanding Nevada’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines
Related Articles: Understanding Nevada’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Nevada’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Nevada’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines
Nevada, known for its arid landscapes and glittering casinos, sits atop a geologically active region. The state’s tectonic history has sculpted its dramatic topography, leaving behind a network of fault lines that continue to shape its present and future. Understanding these fault lines is crucial for comprehending the state’s seismic potential and informing strategies for mitigating earthquake risk.
The Tectonic Tapestry of Nevada
Nevada’s geological story begins millions of years ago, when the North American and Pacific tectonic plates collided. This collision, known as subduction, led to the creation of the Sierra Nevada mountain range and the Basin and Range province, a vast region characterized by alternating mountain ranges and valleys.
The Basin and Range province, encompassing much of Nevada, is defined by a unique geological feature: extensional tectonics. This process, driven by the ongoing westward movement of the Pacific plate, stretches the Earth’s crust, creating faults and causing the land to pull apart. These faults, essentially cracks in the Earth’s surface, act as pathways for the release of built-up stress, often resulting in earthquakes.
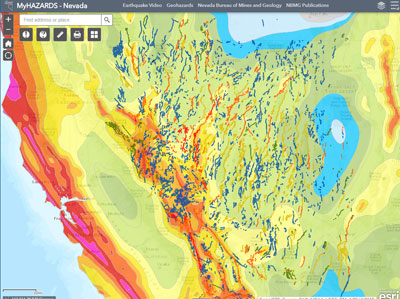
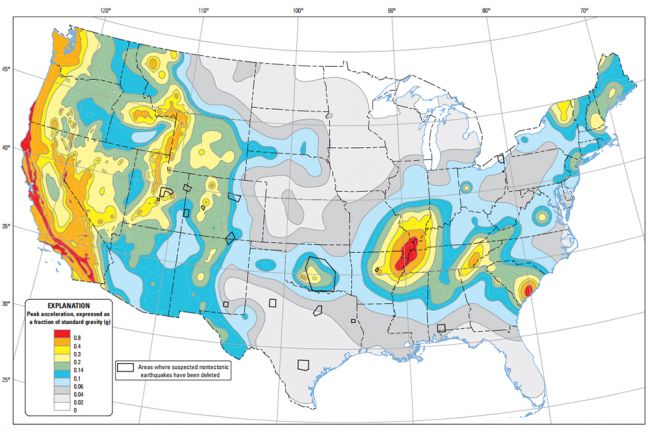
Mapping Nevada’s Fault Lines: A Vital Tool for Understanding Seismic Hazards
Maps depicting the distribution of fault lines in Nevada are invaluable tools for understanding the state’s seismic potential. These maps, compiled through geological surveys and analysis of earthquake data, provide a visual representation of the zones most vulnerable to earthquakes.
Key Fault Lines in Nevada
Several major fault lines traverse Nevada, each posing a significant seismic threat:
-
Walker Lane Fault Zone: This major fault zone runs along the eastern edge of the Sierra Nevada, extending south into California. It is considered one of the most active fault zones in the western United States, responsible for numerous earthquakes throughout history.
-
Owens Valley Fault Zone: Located in eastern California, this fault zone extends into Nevada, bordering the eastern edge of the Sierra Nevada. It has produced several significant earthquakes, including the 1872 Owens Valley earthquake, which remains the largest recorded earthquake in California history.
-
Garlock Fault: Situated in southern California, the Garlock Fault extends into Nevada, running parallel to the San Andreas Fault. It is a significant source of seismic activity, capable of generating powerful earthquakes.
-
Earthquake Lake Fault: This fault is located in the central part of Nevada, near the town of Hawthorne. It is known for its association with the 1915 Earthquake Lake earthquake, which caused a massive landslide and formed the namesake Earthquake Lake.
-
Dixie Valley-Fairview Valley Fault Zone: This fault zone extends across central Nevada, running north-south. It has been responsible for several notable earthquakes, including the 1954 Dixie Valley earthquake.
Understanding the Significance of Fault Lines in Nevada
The presence of these major fault lines highlights Nevada’s susceptibility to earthquakes. Understanding the location and characteristics of these faults is crucial for several reasons:
-
Earthquake Prediction and Mitigation: Fault line maps provide valuable insights into the location and potential magnitude of future earthquakes. This information is crucial for developing effective earthquake prediction and mitigation strategies.
-
Infrastructure Design and Development: Knowledge of fault lines is essential for designing and constructing earthquake-resistant buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure. This helps ensure the safety and resilience of communities in the event of an earthquake.
-
Land Use Planning: Fault line maps play a significant role in land use planning, guiding the development of safe and sustainable communities. By identifying areas prone to seismic activity, planners can minimize the risk of potential damage and loss of life.
-
Public Awareness and Education: Fault line maps raise public awareness of seismic hazards, encouraging individuals and communities to prepare for potential earthquakes. This includes understanding earthquake preparedness measures and practicing emergency drills.
FAQs about Fault Lines in Nevada
Q: Are earthquakes common in Nevada?
A: Yes, Nevada experiences a significant number of earthquakes each year. The state’s location within the Basin and Range province, characterized by numerous fault lines, makes it prone to seismic activity.
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Nevada?
A: Nevada experiences a wide range of seismic activity, from small tremors to major earthquakes. The frequency and magnitude of earthquakes vary depending on the specific fault zone and the amount of stress accumulated.
Q: What is the largest earthquake recorded in Nevada?
A: The largest earthquake recorded in Nevada was the 1915 Earthquake Lake earthquake, estimated to have had a magnitude of 7.3.
Q: How can I prepare for an earthquake in Nevada?
A: Earthquake preparedness involves several steps, including securing heavy objects, creating an emergency kit, and developing a family communication plan. It is also crucial to learn about local evacuation routes and emergency shelters.
Q: What are the potential consequences of a major earthquake in Nevada?
A: A major earthquake in Nevada could cause significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and utilities. It could also trigger landslides, fires, and tsunamis in coastal areas.
Tips for Understanding and Mitigating Earthquake Risks in Nevada
-
Learn about the fault lines in your area: Familiarize yourself with the location and characteristics of nearby fault lines. This information can help you assess your individual earthquake risk.
-
Secure your home: Take steps to secure heavy objects, such as bookcases and mirrors, to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
-
Develop an emergency plan: Create a family communication plan and assemble an emergency kit containing essential supplies, such as food, water, and first-aid supplies.
-
Practice earthquake drills: Regularly practice earthquake drills to prepare for a potential earthquake.
-
Stay informed: Stay updated on earthquake preparedness resources and information from local authorities and emergency management agencies.
Conclusion
Nevada’s fault lines serve as a reminder of the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust. Understanding these geological features is crucial for mitigating earthquake risks and ensuring the safety and resilience of communities. By utilizing fault line maps, promoting public awareness, and implementing effective earthquake preparedness strategies, Nevada can minimize the impact of future seismic events and safeguard its residents and infrastructure.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Nevada’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to the State’s Fault Lines. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
