Understanding Soil Temperature Variations In Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Soil Temperature Variations in Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Soil Temperature Variations in Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Soil Temperature Variations in Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Soil Temperature Variations in Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Soil Temperature Variations in Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Importance of Soil Temperature Mapping
- 3.2 Factors Influencing Soil Temperature in Missouri
- 3.3 Understanding Soil Temperature Maps: Key Components
- 3.4 Applications of Soil Temperature Maps in Missouri Agriculture
- 3.5 FAQs about Soil Temperature Maps in Missouri
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Soil Temperature Maps in Missouri Agriculture
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Soil Temperature Variations in Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide

Soil temperature, a crucial factor influencing plant growth and agricultural practices, exhibits significant spatial and temporal variations across Missouri. Understanding these variations is paramount for optimizing crop yields, managing pests and diseases, and ensuring sustainable agricultural practices. This article delves into the intricacies of soil temperature mapping in Missouri, exploring its significance, applications, and insights it provides into the state’s agricultural landscape.
The Importance of Soil Temperature Mapping
Soil temperature maps are invaluable tools for agricultural professionals, researchers, and policymakers. They provide a comprehensive overview of soil temperature distribution across a region, highlighting areas with distinct thermal regimes. These maps are instrumental in:
- Optimizing Crop Selection: Different crops have specific temperature requirements for germination, growth, and maturation. Soil temperature maps enable farmers to select crops best suited to the prevailing thermal conditions in their fields, maximizing yield potential and reducing risks associated with unsuitable temperatures.
- Precision Agriculture: Soil temperature data allows for precise application of fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing environmental impact. By tailoring management practices to specific soil temperature zones, farmers can enhance efficiency and sustainability.
- Pest and Disease Management: Soil temperature influences the lifecycle and prevalence of pests and diseases. Maps can help predict areas prone to specific pest infestations or disease outbreaks, enabling proactive management strategies.
- Climate Change Assessment: Soil temperature data is essential for monitoring the impact of climate change on agricultural ecosystems. By analyzing trends over time, researchers can assess the vulnerability of Missouri’s agriculture to rising temperatures and develop adaptation strategies.
Factors Influencing Soil Temperature in Missouri
Several factors contribute to the spatial and temporal variations in soil temperature across Missouri:
- Latitude: Missouri spans a significant latitudinal range, resulting in a gradient of solar radiation and temperature. Northern Missouri experiences cooler temperatures compared to the southern regions.
- Elevation: Higher elevations generally experience lower temperatures due to thinner atmosphere and reduced solar radiation. Missouri’s Ozark Plateau, with its elevated terrain, exhibits distinct temperature patterns compared to the lowlands.
- Topography: Slopes facing south receive more direct sunlight and experience warmer temperatures compared to north-facing slopes. This aspect plays a significant role in shaping microclimates and soil temperature variations within fields.
- Soil Type: Different soil types have varying thermal properties. Sandy soils warm up and cool down faster compared to clay soils, which retain heat for longer periods.
- Vegetation Cover: Dense vegetation cover provides shade and reduces soil temperature fluctuations. Conversely, bare soil surfaces experience greater temperature extremes.
- Weather Patterns: Air temperature, rainfall, and cloud cover significantly influence soil temperature. Hot and sunny days lead to warmer soil temperatures, while cloudy and rainy days promote cooler temperatures.
Understanding Soil Temperature Maps: Key Components
Soil temperature maps typically depict the average soil temperature at a specific depth, usually within the root zone of crops. They often incorporate color gradients or isolines to represent temperature ranges, with warmer areas denoted by darker shades or higher isoline values.
Key components of a soil temperature map include:
- Spatial Resolution: This refers to the level of detail depicted on the map. Higher resolution maps provide more accurate and localized temperature data.
- Time Scale: Soil temperature maps can be generated for specific dates, seasons, or longer periods, allowing for analysis of temporal trends.
- Data Source: Soil temperature data can be obtained from ground-based sensors, weather stations, or remote sensing techniques like satellite imagery.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of soil temperature maps depends on the quality and density of data sources, as well as the methods used for interpolation and visualization.
Applications of Soil Temperature Maps in Missouri Agriculture
Soil temperature maps have numerous applications in Missouri agriculture, contributing to efficient resource management, improved crop production, and sustainable practices:
- Crop Selection and Planting Dates: By analyzing soil temperature maps, farmers can identify areas suitable for specific crops based on their temperature requirements. This information helps determine optimal planting dates, maximizing yield potential and minimizing risks associated with frost damage or heat stress.
- Irrigation Management: Soil temperature maps assist in identifying areas with higher water demand due to warmer soil temperatures. This enables farmers to optimize irrigation schedules, conserving water resources and minimizing irrigation costs.
- Fertilizer Application: Soil temperature influences the availability and uptake of nutrients. Maps can guide farmers in applying fertilizers at appropriate times and locations, maximizing nutrient utilization and minimizing environmental pollution.
- Pest and Disease Control: Understanding soil temperature patterns helps predict areas prone to specific pest infestations or disease outbreaks. This information allows farmers to implement proactive control measures, reducing crop losses and minimizing pesticide use.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Soil temperature maps contribute to sustainable agricultural practices by promoting resource optimization, minimizing environmental impact, and enhancing resilience to climate change.
FAQs about Soil Temperature Maps in Missouri
1. Where can I access soil temperature maps for Missouri?
Soil temperature maps are available from various sources, including:
- Missouri Department of Agriculture: The department often provides soil temperature data and maps related to agricultural applications.
- University of Missouri Extension: The university’s extension service offers resources and information on soil temperature, including maps and data analysis tools.
- National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS): NASS collects and publishes agricultural data, including soil temperature information, at a national level.
- Private Data Providers: Several private companies specialize in providing soil temperature maps and data analysis services for agricultural applications.
2. What is the typical soil temperature range in Missouri?
Soil temperature in Missouri varies significantly depending on location, season, and soil type. However, generally, average soil temperatures in the root zone range from:
- Winter: 40-50°F (4-10°C)
- Spring: 50-65°F (10-18°C)
- Summer: 70-85°F (21-29°C)
- Fall: 50-65°F (10-18°C)
3. How often are soil temperature maps updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the data source and the purpose of the map. Some maps are updated daily, while others may be updated weekly, monthly, or seasonally.
4. How accurate are soil temperature maps?
The accuracy of soil temperature maps depends on the quality and density of data sources, as well as the methods used for interpolation and visualization. Maps based on ground-based sensors or high-resolution satellite imagery generally provide higher accuracy compared to those based on limited data sources.
5. What are the limitations of soil temperature maps?
Soil temperature maps provide valuable insights but have limitations:
- Spatial Resolution: Maps may not capture fine-scale variations in soil temperature within fields.
- Data Availability: Data sources may be limited in certain areas, affecting the accuracy and coverage of maps.
- Temporal Variability: Soil temperature fluctuates constantly, and maps represent averages over specific periods.
Tips for Utilizing Soil Temperature Maps in Missouri Agriculture
- Consult with Experts: Seek guidance from agricultural experts or soil scientists to interpret soil temperature maps and apply the information effectively.
- Consider Local Conditions: Soil temperature maps provide general trends, but local factors like soil type, topography, and vegetation cover can influence actual temperatures.
- Combine with Other Data: Integrate soil temperature maps with other agricultural data, such as rainfall, crop yields, and pest records, for a comprehensive understanding of agricultural conditions.
- Monitor Soil Temperature: Utilize soil temperature sensors to monitor actual temperatures in fields and validate map data.
- Adapt to Changing Conditions: As climate change impacts soil temperature patterns, regularly update and adjust agricultural practices based on the latest map data.
Conclusion
Soil temperature maps are powerful tools for understanding and managing the agricultural landscape of Missouri. By providing insights into soil temperature variations, these maps enable farmers to optimize crop selection, irrigation, fertilization, and pest control practices, contributing to increased efficiency, sustainability, and resilience in Missouri’s agriculture. As technology advances and data sources improve, soil temperature maps will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of Missouri’s agricultural sector.




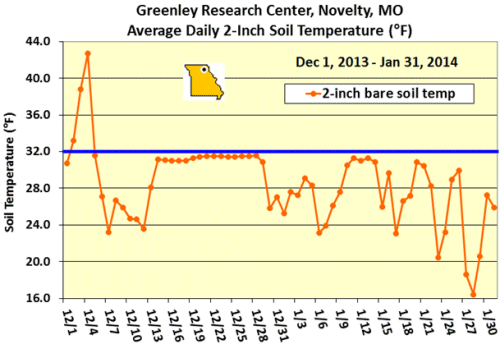
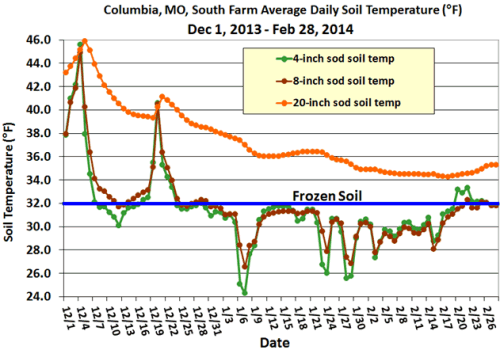

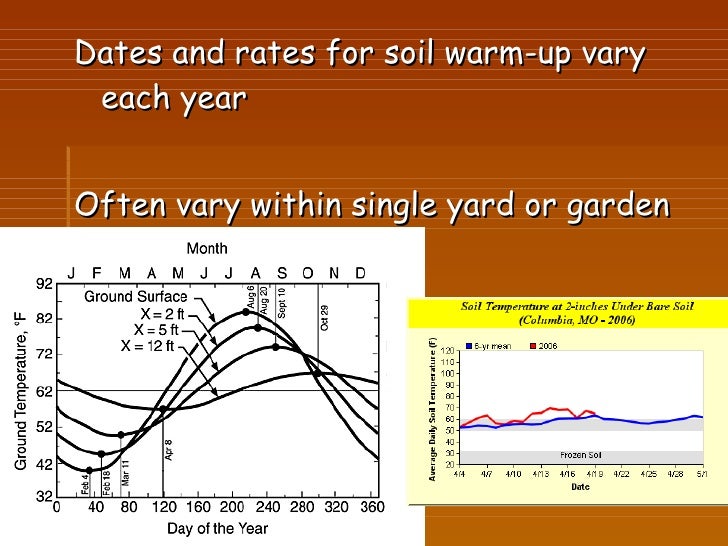
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Soil Temperature Variations in Missouri: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!