Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographic Journey Through West Virginia
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographic Journey Through West Virginia
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographic Journey Through West Virginia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographic Journey Through West Virginia
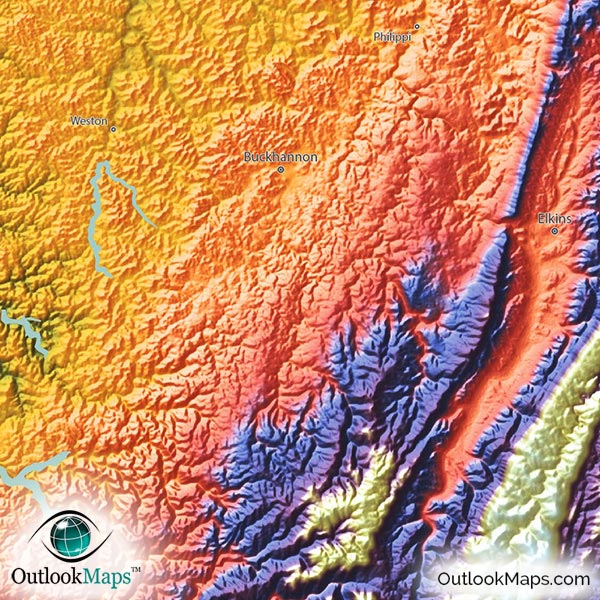
West Virginia, a state known for its rugged beauty and rich history, presents a diverse landscape sculpted by ancient forces. Understanding this intricate tapestry of mountains, valleys, and rivers is crucial for appreciating the state’s natural wonders and navigating its challenges. This exploration delves into the world of topographic maps, essential tools for deciphering West Virginia’s terrain and its impact on various aspects of life.
Deciphering the Terrain: A Topographic Map’s Language
Topographic maps, often referred to as "topo maps," are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, showcasing both elevation and landforms. They are not simply static images but intricate systems of symbols and lines that translate complex three-dimensional data into a two-dimensional format.
Contour Lines: The Key to Elevation
The foundation of a topographic map lies in contour lines. These lines connect points of equal elevation, forming a web that outlines the shape of the land. The closer the contour lines are together, the steeper the terrain. Conversely, widely spaced lines indicate a gentle slope.
Understanding the Colors and Symbols
Beyond contour lines, topographic maps employ a variety of colors and symbols to represent different features:
- Green: Typically represents forests and woodlands.
- Blue: Depicts water bodies, including rivers, lakes, and streams.
- Brown: Represents areas of bare ground, rock outcrops, and desert landscapes.
- Black: Represents roads, buildings, and other man-made structures.
Additional symbols, often found in a legend or key, denote specific features like bridges, power lines, and even historical landmarks.
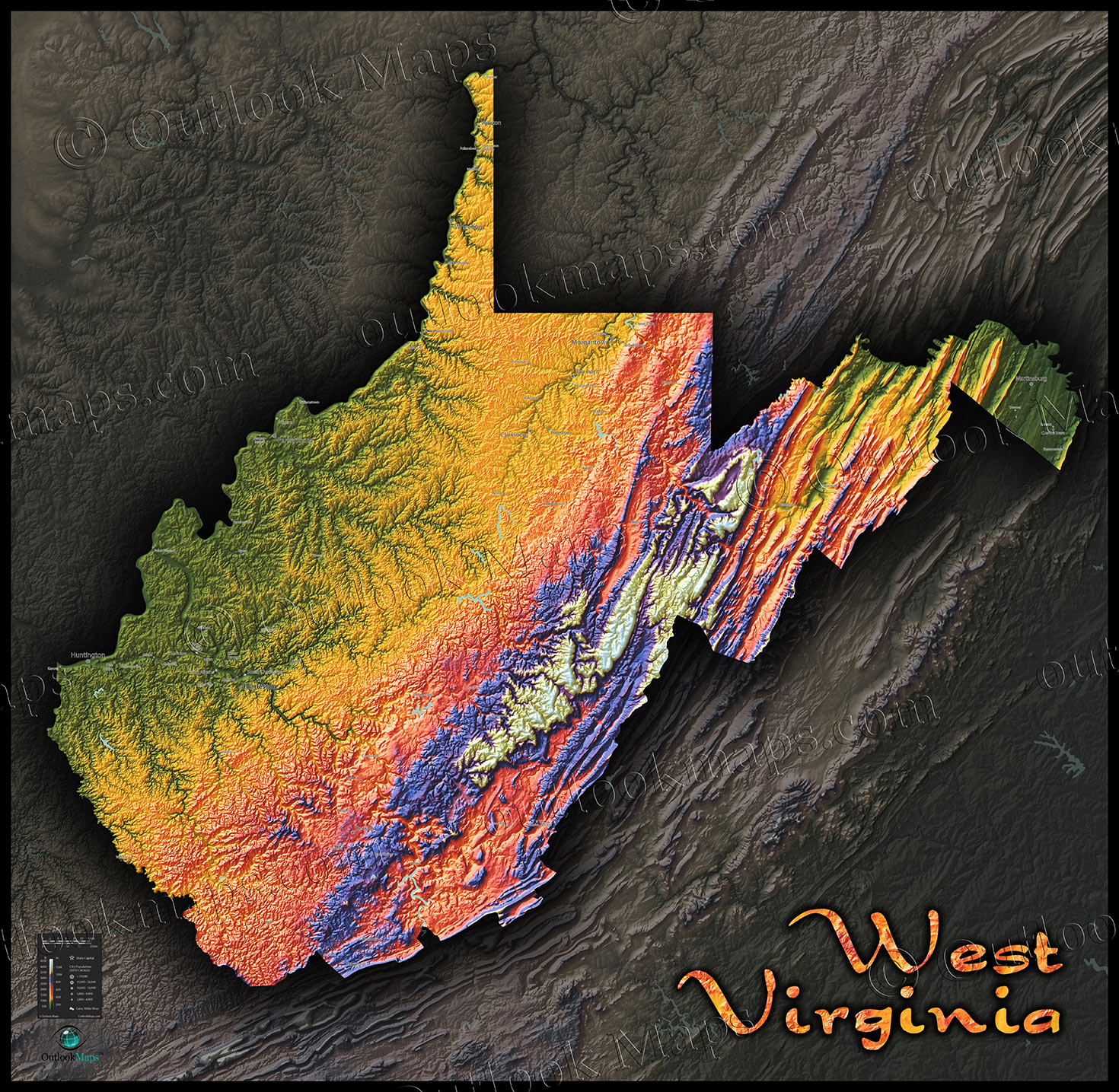
West Virginia’s Topographic Signature: A Landscape Shaped by Time
West Virginia’s topography is a testament to its geological history. The Appalachian Mountains, a defining feature of the eastern United States, traverse the state, creating a rugged landscape characterized by steep slopes, deep valleys, and numerous rivers and streams.
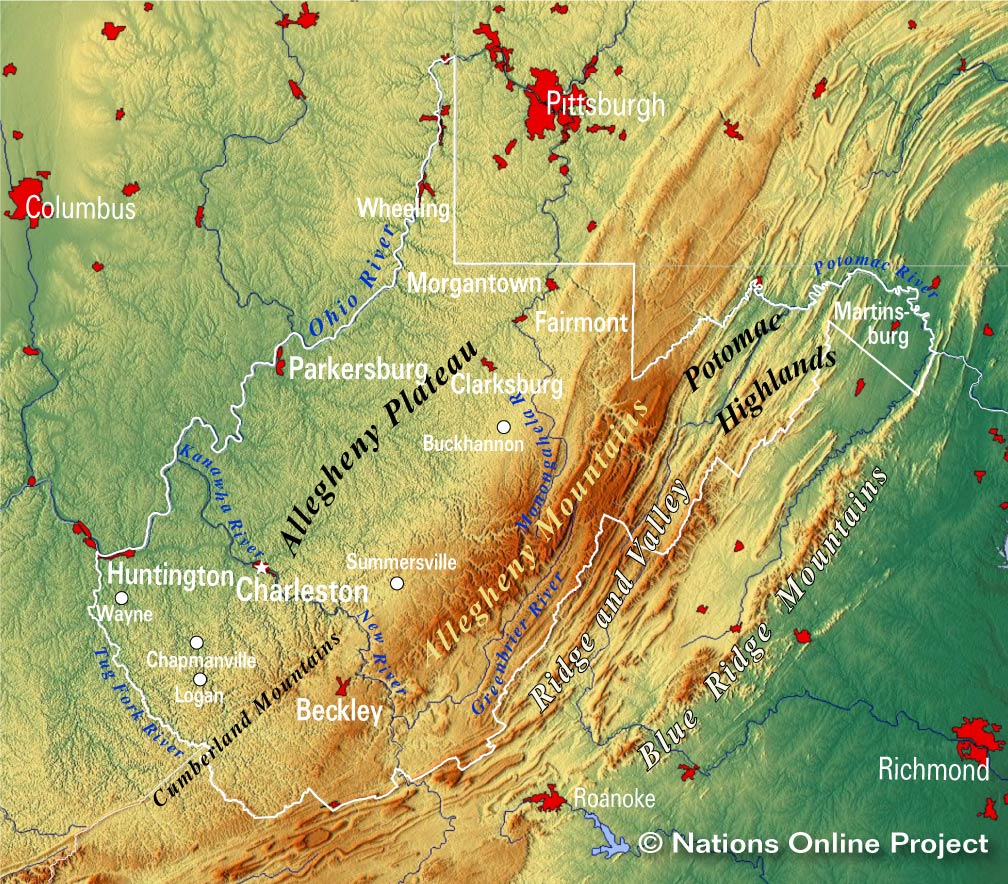
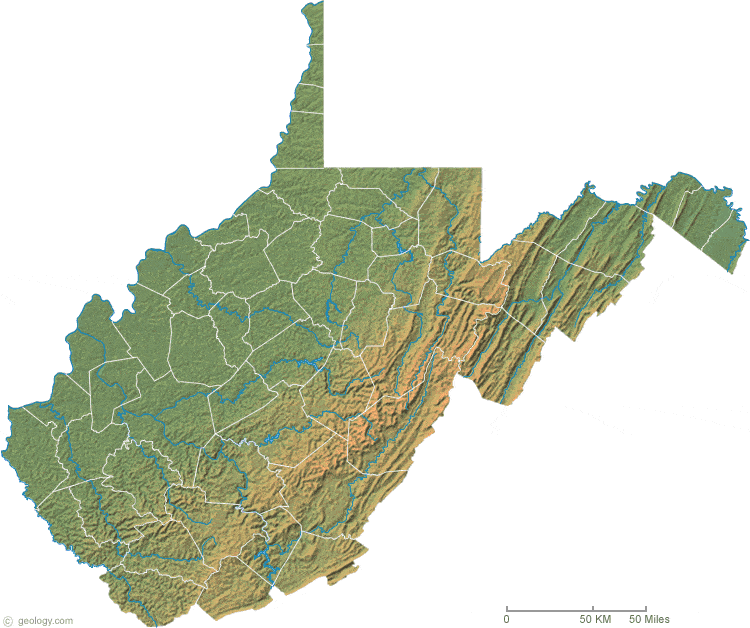
The Appalachian Plateau: A Plateau with a Twist
The western part of West Virginia is dominated by the Appalachian Plateau, a vast, elevated region with a relatively flat surface. However, this plateau is not entirely uniform. It is dissected by numerous rivers and streams, creating a complex network of valleys and ridges. The New River Gorge National River, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a prime example of this unique landscape.
The Allegheny Mountains: A Spine of Rugged Beauty
The Allegheny Mountains form the eastern boundary of West Virginia. These mountains are older and more eroded than the Appalachian Plateau, resulting in a landscape of rounded peaks and deep valleys. The state’s highest point, Spruce Knob, stands tall within this range.
The Importance of Topography in West Virginia
Understanding West Virginia’s topography is crucial for various reasons:
- Resource Management: The state’s diverse terrain influences its natural resources, including forests, minerals, and water. Topographic maps help resource managers assess the potential and limitations of these resources.
- Infrastructure Development: Roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects must be carefully planned to accommodate the challenging terrain. Topographic maps provide essential data for designing and constructing these projects safely and efficiently.
- Environmental Protection: Topographic maps play a vital role in understanding the flow of water and the movement of sediment. This information is critical for protecting water quality, mitigating erosion, and managing natural disasters.
- Recreation and Tourism: West Virginia’s rugged beauty attracts outdoor enthusiasts. Topographic maps are indispensable for planning hiking trails, navigating rivers, and exploring the state’s many natural wonders.
- Emergency Response: In the event of natural disasters, topographic maps help emergency responders understand the terrain and plan effective rescue and relief efforts.
FAQs: Exploring West Virginia’s Topographic Map
Q: What is the best source for obtaining topographic maps of West Virginia?
A: The United States Geological Survey (USGS) is a primary source for topographic maps. Their website offers a wide range of maps at various scales, including those specifically designed for West Virginia.
Q: Are there online tools for viewing and interacting with topographic maps?
A: Yes, several online mapping tools allow users to view and interact with topographic maps. Popular options include Google Earth, ArcGIS Online, and the USGS TopoView. These tools offer features like zooming, panning, and elevation profiles, enhancing the user experience.
Q: How can I use a topographic map to plan a hiking trip?
A: Topographic maps are essential for planning hiking trips. By studying the contour lines, you can identify the elevation changes and potential difficulties of a trail. You can also use the symbols to locate water sources, campsites, and other points of interest.
Q: What are some common challenges associated with navigating West Virginia’s terrain?
A: West Virginia’s terrain presents several challenges for navigation. Steep slopes, dense vegetation, and the presence of streams and rivers can all pose obstacles. It is crucial to be aware of these challenges and to plan accordingly.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps in West Virginia
- Familiarize Yourself with the Symbols: Before venturing into the wilderness, spend time studying the legend or key of the topographic map. Understanding the symbols will ensure you can accurately interpret the information presented.
- Consider the Scale: Choose a map scale that suits your needs. For detailed exploration, a larger scale map is recommended. For broader overview, a smaller scale map might be sufficient.
- Carry a Compass and GPS: While topographic maps provide valuable information, it is always wise to carry a compass and a GPS device for additional navigation support, especially in remote areas.
- Respect the Environment: When using topographic maps for outdoor recreation, remember to respect the environment. Stay on designated trails, avoid disturbing wildlife, and pack out all trash.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery Through Topography
Topographic maps are not mere static images; they are powerful tools that unlock the secrets of West Virginia’s landscape. They reveal the hidden stories of its geological history, guide resource management, inform infrastructure development, and enhance our appreciation for the state’s natural wonders. By understanding the language of contour lines, colors, and symbols, we can embark on a journey of discovery through the intricate topography of West Virginia, appreciating its unique character and the challenges and opportunities it presents.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Topographic Journey Through West Virginia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!