Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Physical Features on Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Physical Features on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Physical Features on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Physical Features on Maps
Maps, the visual representations of our world, are more than just lines and colors. They are intricate frameworks that capture the complexities of our planet, showcasing not just political boundaries but also the natural wonders that define it. These natural wonders, known as physical features, are the building blocks of our planet’s landscape, shaping its ecosystems, influencing human settlements, and inspiring awe in those who encounter them.
Defining the Terrain: What are Physical Features?
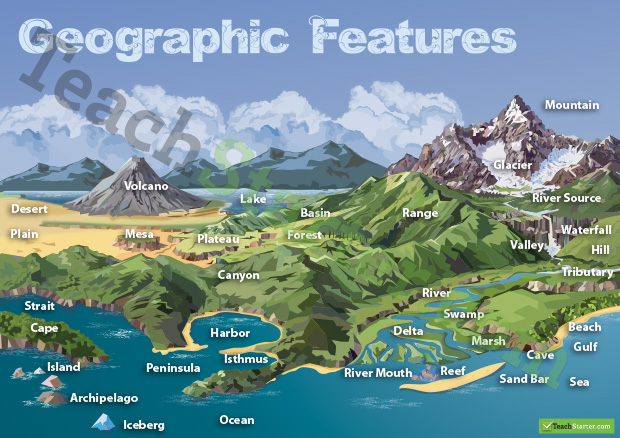
Physical features, often referred to as landforms, are the natural elements that constitute the Earth’s surface. They encompass a wide array of formations, each with unique characteristics and significance. Mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, oceans, deserts, and forests are just a few examples of the diverse features that adorn our planet.
These features are formed through a complex interplay of geological processes, including tectonic plate movements, erosion, weathering, and deposition. Over millions of years, these forces have sculpted the Earth’s surface, creating the dramatic landscapes we see today.
A Window into Earth’s History: The Significance of Physical Features
Understanding physical features goes beyond mere observation. They provide valuable insights into Earth’s history, revealing the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet over eons.
- Geological Insights: The presence of mountains, for instance, speaks to the collision of tectonic plates, highlighting the immense power of these geological forces. Similarly, the meandering course of a river reveals the erosive power of water over time, shaping the landscape and influencing the flow of life.
- Ecological Diversity: Physical features are the foundation of Earth’s diverse ecosystems. Mountains create microclimates, supporting unique flora and fauna adapted to their harsh conditions. Rivers and lakes provide vital habitats for aquatic life, while forests serve as carbon sinks and havens for countless species.
- Human Influence: Physical features have played a crucial role in shaping human civilization. Mountains have served as natural barriers, influencing trade routes and cultural development. Rivers have provided water for agriculture and transportation, fostering the growth of settlements and empires.
Navigating the Landscape: The Importance of Physical Features on Maps
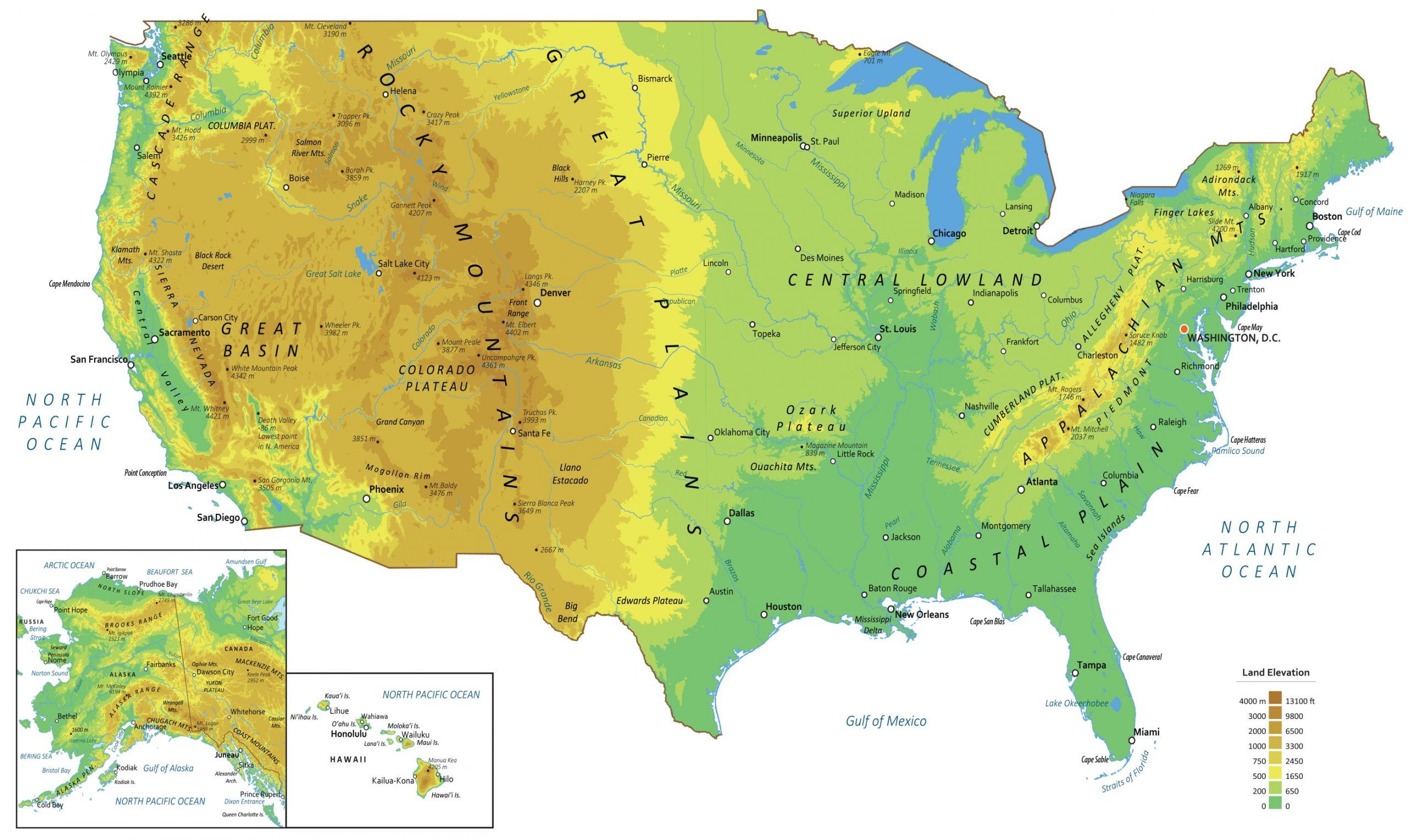
Maps, as visual representations of the Earth, incorporate physical features to provide a comprehensive understanding of the landscape. They serve as essential tools for navigation, exploration, and resource management.
- Navigation: Physical features act as landmarks, guiding travelers across vast distances. Mountains, rivers, and coastlines provide recognizable points of reference, enabling efficient navigation, particularly in areas with limited infrastructure.
- Resource Management: Maps showcasing physical features are vital for managing natural resources. Identifying water sources, fertile land, and mineral deposits helps in optimizing resource utilization and ensuring sustainable development.
- Environmental Understanding: By visualizing physical features, maps facilitate environmental understanding and conservation efforts. They highlight areas prone to natural hazards, such as floods, landslides, and earthquakes, enabling informed planning and mitigation strategies.
Delving Deeper: Exploring Specific Physical Features
Let’s delve into some specific physical features and their significance:
1. Mountains:
- Formation: Mountains are formed through the collision of tectonic plates, causing the Earth’s crust to buckle and fold.
- Significance: They act as natural barriers, influencing climate patterns, creating diverse ecosystems, and shaping human settlements.
- Examples: The Himalayas, the Andes, the Alps.
2. Valleys:
- Formation: Valleys are formed by erosion, typically by rivers or glaciers.
- Significance: They provide fertile land for agriculture, act as pathways for transportation, and offer scenic beauty.
- Examples: The Nile Valley, the Valley of the Kings, Yosemite Valley.
3. Rivers:
- Formation: Rivers originate from rainfall or melting snow and flow downhill, carving channels through the landscape.
- Significance: They provide water for agriculture, transportation, and hydroelectric power, supporting diverse ecosystems.
- Examples: The Amazon River, the Mississippi River, the Yangtze River.
4. Lakes:
- Formation: Lakes can be formed by tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, or glacial erosion.
- Significance: They provide freshwater resources, support aquatic life, and offer recreational opportunities.
- Examples: Lake Superior, Lake Baikal, Lake Victoria.
5. Oceans:
- Formation: Oceans cover 71% of the Earth’s surface, formed by the accumulation of water over millions of years.
- Significance: They regulate climate, support marine life, and provide resources for transportation and trade.
- Examples: The Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean.
6. Deserts:
- Formation: Deserts are characterized by extremely low rainfall, caused by various factors including mountain ranges and dry air currents.
- Significance: They support unique ecosystems adapted to arid conditions and hold valuable mineral resources.
- Examples: The Sahara Desert, the Atacama Desert, the Gobi Desert.
7. Forests:
- Formation: Forests are characterized by dense tree cover, influenced by climate and soil conditions.
- Significance: They act as carbon sinks, provide timber resources, and support diverse ecosystems.
- Examples: The Amazon Rainforest, the Congo Rainforest, the Siberian Taiga.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q1: What are some examples of physical features on a map?
A1: Mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, oceans, deserts, forests, plains, plateaus, and canyons are all common examples of physical features on a map.
Q2: How do physical features influence human settlements?
A2: Physical features often dictate where humans settle. For example, fertile valleys provide suitable land for agriculture, while rivers offer transportation routes and water sources. Conversely, harsh mountain environments may limit settlement.
Q3: How do physical features affect climate?
A3: Physical features significantly influence climate. Mountains create rain shadows, leading to drier conditions on one side. Oceans regulate temperature and influence precipitation patterns.
Q4: How can maps help in understanding environmental issues?
A4: Maps that showcase physical features can highlight areas vulnerable to natural disasters, identify areas of biodiversity, and track changes in land use over time, providing valuable insights for environmental management.
Q5: What are some resources that can be found in physical features?
A5: Physical features are rich in resources. Mountains contain mineral deposits, rivers provide water for agriculture and hydropower, forests offer timber and medicinal plants, and oceans provide seafood and energy resources.
Tips for Understanding Physical Features on Maps
- Look for symbols and colors: Maps often use specific symbols and colors to represent different physical features. Refer to the map legend to understand the meaning of each symbol.
- Consider the scale: The scale of the map influences the level of detail. Large-scale maps show more detail, while small-scale maps provide an overview of larger areas.
- Pay attention to elevation: Contour lines on a map indicate changes in elevation, revealing the topography of the land.
- Use online resources: Interactive maps and online databases provide comprehensive information about physical features, including their formation, characteristics, and significance.
Conclusion: Embracing the Landscape
Physical features are the defining elements of our planet’s landscape, shaping its history, influencing its ecosystems, and guiding human development. Understanding these features is crucial for navigation, resource management, and environmental conservation. Maps, as visual representations of the Earth, play a vital role in highlighting these features, providing insights into the intricate web of life that thrives on our planet. By embracing the knowledge of physical features, we can better appreciate the beauty and complexity of our world, making informed decisions for a sustainable future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Physical Features on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!